Non-coding RNAs as key regulators in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40625740
- PMCID: PMC12230020
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602252
Non-coding RNAs as key regulators in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: Non-coding RNAs as key regulators in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1653985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1653985. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40698072 Free PMC article.
Abstract
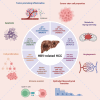
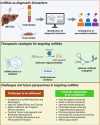
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a significant global health challenge due to its high prevalence and poor prognosis. Recent advances have revealed that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including microRNAs, long ncRNAs, circular RNAs, and small nucleolar RNAs, play critical regulatory roles in HBV-induced oncogenesis. These ncRNAs modulate various cancer hallmarks and contribute to HCC progression. Notably, their stability, detectability in bodily fluids, and disease-specific expression patterns render these ncRNAs as highly promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for HBV-HCC. Herein, we review the types and mechanisms of HBV-related ncRNAs, emphasizing their dual roles as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Furthermore, we discuss their applicability as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets and review recent directions in ncRNA-based approaches that aim to enhance patient treatment. Concerning these aspects, the present review aimed to provide an understanding of the complexity of ncRNAs in HBV-related HCC with the hope of directing future research and developments towards effective control of this complex malignancy known as HCC.
Keywords: biomarkers; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; non-coding RNAs; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Ramalingam, Zhang, Hussain, Khan, Mawkili, Hanbashi, Gupta, Balakrishnan and Arumugam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang. S, Fu. X, He. S, Zou. J, Luo. Y, Li. G, et al. Global infectious diseases in june 2023: monthly analysis. Zoonoses. (2024) 3:30. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2023-1007 - DOI
-
- Zheng P, Xu D, Cai Y, Zhu L, Xiao Q, Peng W, et al. A multi-omic analysis reveals that Gamabufotalin exerts anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effects by regulating amino acid metabolism through targeting STAMBPL1. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2024) 135:156094. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156094 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

