Recent advances in glycopeptide hydrogels: design, biological functions, and biomedical applications
- PMID: 40625852
- PMCID: PMC12230054
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1577192
Recent advances in glycopeptide hydrogels: design, biological functions, and biomedical applications
Abstract
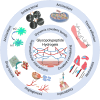
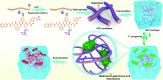
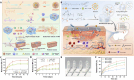
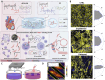
Glycopeptide hydrogels, biomaterials constructed from polysaccharides and peptides through dynamic covalent bonding and supramolecular interactions, mimic the structure and functions of the natural extracellular matrix. Their three-dimensional network structure endows them with remarkable mechanical resilience, self-healing capacity, and stimuli-responsive behavior, enabling diverse biomedical applications in tissue regeneration, wound healing, drug delivery, and antimicrobial therapies. This review comprehensively examines design principles for engineering glycopeptide hydrogels, encompassing biomolecular selection criteria and dynamic crosslinking methodologies. We analyze their multifunctional properties including antimicrobial efficacy, immunomodulation, antioxidant activity, tissue adhesion, and angiogenic potential, while highlighting smart drug release mechanisms. Applications in regenerative medicine are critically assessed, particularly in cutaneous wound healing, bone and cartilage reconstruction, myocardial repair, and neural regeneration. Finally, we delineate future directions to advance glycopeptide hydrogels, emphasizing functional sequence expansion of bioactive motifs, high-fidelity biomechanical mimicry of natural tissues, and precise simulation of organ-specific microenvironments for next-generation precision medicine.
Keywords: dynamic hydrogel; injectable hydrogel; self-assembling peptide hydrogel; supramolecular hydrogel; tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zou and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advances in Composite Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels for Wound Healing: Mechanisms and Applications.Gels. 2025 May 31;11(6):420. doi: 10.3390/gels11060420. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40558719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial, self-healing, and pH-responsive PVA/ZIF-8@tannic acid nanocomposite hydrogel for sustained delivery of garlic extract.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07752-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595265 Free PMC article.
-
A photothermal-enhanced thermoelectric nanosheet incorporated with zwitterionic hydrogels for wound repair and bioelectronics.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 15;200:610-628. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.033. Epub 2025 May 12. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40368059
-
An ovalbumin-based hydrogel loaded with dendrobium polysaccharide for promoting wound healing while reducing inflammations.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21825. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06717-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595006 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Injectable Hydrogel Biotherapeutics for Regenerative Dental Medicine.Macromol Biosci. 2025 Jul 2:e00096. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202500096. Online ahead of print. Macromol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40605036 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

