Relationship Between Social Support, Symptom Burden, Dyspnea, Perceived Stress, Perceived Stigma, Coping Styles, and Psychological Distress in Patients with Stable COPD: A Structural Equation Model
- PMID: 40626316
- PMCID: PMC12233022
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S521786
Relationship Between Social Support, Symptom Burden, Dyspnea, Perceived Stress, Perceived Stigma, Coping Styles, and Psychological Distress in Patients with Stable COPD: A Structural Equation Model
Abstract
Background: Psychological distress is prevalent in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and may contribute to disease progression. However, the interplay among its influencing factors remains unclear. This study aimed to explore how social support, symptom burden, dyspnea, perceived stress, perceived stigma, and coping styles impact psychological distress in stable COPD using a structural equation model (SEM).
Methods: A convenience sample of 386 stable COPD patients was recruited from three tertiary hospitals in Chongqing, China. Data were collected using Distress Thermometer, Perceived Social Support Scale, COPD Assessment Test, the Modified Medical Research Council Dyspnea Score, the Perceived Stress Scale 10-item version, the Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness 8-item version, and the Simplified Coping Style Questionnaire were used for data collection. SEM was used for relationships among variables.
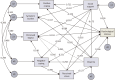
Results: The mean psychological distress score was (3.770 ± 1.525). Positive coping style (β = -0.329, p < 0.001) and perceived social support (β = -0.750, p < 0.001) reduced psychological distress directly. In contrast, negative coping style (β = 0.360, p < 0.001), symptom burden (β = 0.317, p < 0.001), dyspnea (β = 0.396, p < 0.001), perceived stress (β = 0.268, p < 0.001), and stigma (β = 0.224, p < 0.001) increased it. Perceived social support exerted extensive indirect effects on psychological distress (total effect = -1.044) by reducing symptom burden (β = -0.681), dyspnea (β = -0.673), and negative coping style (β = -0.726), and by improving positive coping style (β = 0.781) and perceived stress (β = -0.688). Similarly, symptom burden indirectly influenced distress via coping styles (indirect effect = 0.290).
Conclusion: Psychological distress in stable COPD patients is influenced by interrelated factors, with perceived social support playing a central role. Healthcare interventions should focus on improving coping strategies, managing symptoms, and strengthening social support to alleviate distress.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; influencing factors; psychological distress; pulmonary disease; structural equation model.
© 2025 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Xu Tian and Lijuan Yi contributed equally to this work as the joint first author. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Structural Equation Model of the Relationship Between Symptom Burden, Psychological Resilience, Coping Styles, Social Support, and Psychological Distress in Elderly Patients With Acute Exacerbation Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in China.Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2024 Aug;18(3):231-237. doi: 10.1016/j.anr.2024.06.003. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2024. PMID: 38908429
-
Association of Patient-Reported Outcome Patterns and Major Clinical Factors with Frailty in Stable COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jun 12;20:1927-1937. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S517270. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40529222 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring psychological distress among lung cancer patients through the stress system model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27253. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09847-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715189 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 23;2015(2):CD003793. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003793.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25705944 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve adherence to pharmacological therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 8;9(9):CD013381. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013381.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34496032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death; 2020. [updated December 9, 2020]. Available from: www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed July 26, 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

