Human Kallikrein 2: A Novel Lineage-Specific Surface Target in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 40627156
- PMCID: PMC12580770
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-25-0950
Human Kallikrein 2: A Novel Lineage-Specific Surface Target in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Targeted therapies for metastatic prostate cancer are limited, highlighting the need for novel drug targets and mechanisms of action (MoA). Human kallikrein 2 (KLK2) is a prostate-specific antigen expressed across the prostate cancer disease continuum. However, it was not recognized as a therapeutic target for prostate cancer in the past due to limited evidence of its cell surface expression. In this study, we systematically characterized KLK2 expression in prostate cancer, confirmed its cell surface expression, and demonstrated the preclinical efficacy of three KLK2-targeting therapeutics with distinct MoA.
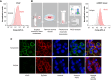
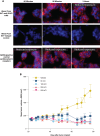
Experimental design: The KLK2 expression profile in different stages of prostate cancer and its cell surface expression were confirmed by IHC and multiplex immunofluorescent staining. The preclinical efficacy of three KLK2-targeting therapeutics was characterized using in vitro prostate cancer cell lines, patient-derived material, and in vivo xenograft mouse models.
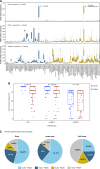
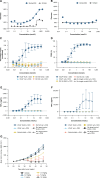
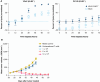
Results: KLK2 was found to be robustly and homogeneously expressed in localized prostate cancer and metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, whereas some heterogeneity was observed in the visceral lesions of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. KLK2 expression was more specific than that of other prostate cancer target antigens. Although KLK2 is traditionally described as a secreted protease, our results demonstrated its cell surface expression in both prostate cancer cell lines and patient-derived tumors. Notably, targeting KLK2 with three different MoAs, including bispecific T-cell redirector, targeted α-radioligand, and autologous chimeric antigen receptor T cells, showed potent in vitro activity and robust in vivo tumor control.
Conclusions: Our study establishes KLK2 as a highly prostate-specific cell surface target. Targeting KLK2 with various MoAs represents novel therapeutic approaches for advanced prostate cancer. See related commentary by Blinka and Yu, p. 4393.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
F. Shen reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. R. Smith reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. T. McDevitt reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. K. Menard reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. S. Tian reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. G. Chu reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. R. Chaudhary reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. J. McCann reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. H. Oyer reports other support from Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine outside the submitted work. S.C. Wang reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. P. Francis reports other support from Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. W.K. Kelly reports grants from Janssen during the conduct of the study as well as nonfinancial support from Janssen and Amgen outside the submitted work. C.G. Drake reports other support from Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other author.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute . Cancer stat facts: prostate cancer. National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program (2024). [cited 2024 Jul 10]. Available from:https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

