Long-Term Real-World Use of Cabotegravir/Rilpivirine: Adherence and Virological Efficacy over a 44-Month Observation Period
- PMID: 40627265
- PMCID: PMC12339819
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-025-01178-3
Long-Term Real-World Use of Cabotegravir/Rilpivirine: Adherence and Virological Efficacy over a 44-Month Observation Period
Abstract
Introduction: Long-acting cabotegravir/rilpivirine (LA-CAB/RPV) offers an effective alternative to daily oral antiretroviral therapy (ART) for people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH), especially those with adherence challenges. Despite increasing use of LA-CAB/RPV, long-term real-world data on durability, adherence, and virological outcomes remain limited to 2 years. This study provides detailed longitudinal data at the individual PLWH level, assessing adherence, safety, and efficacy over a period of up to 10 years.
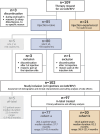
Methods: All PLWH receiving LA-CAB/RPV at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf between 2021 and 2025 were analyzed over 44 months, including injection-naïve individuals and former registration trial participants. Clinical, laboratory, immunological, and virological data were reviewed.
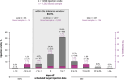
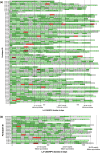
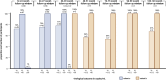
Results: In total, 102 PLWH received ≥ 2 LA-CAB/RPV injections: (a) 77 injection-naïve and (b) 20 injection-experienced participants from clinical trials; and 5 off-label treated participants who were analyzed separately. Among participants treated in-label, 84% (1417/1690) of injections were administered on time. However, 82% of all participants (80/97) experienced ≥ 1 delay, with 96% (77/80) of delays limited to 8-14 days. Virological suppression (VL < 50 copies/mL) was achieved by 97% throughout the observation period (94/97). In total, 14% (14/97), all of cohort (a), discontinued injection therapy and switched back to oral ART. Injection site reactions were reported by 64%, while mild systemic side effects occurred in 41% at some point, most commonly neuropsychiatric symptoms in those with a history of depression. One confirmed virological failure (CVF) occurred after 40 months in cohort (a); two CVFs were observed in the small off-label-treated subgroup.
Conclusions: This real-world study, with a 44-month observation period and follow-up of up to 10 years on LA-CAB/RPV, confirms its long-term efficacy and safety, supporting its durability as a maintenance option for PLWH, even with occasional delays and slightly lower adherence than seen in clinical trials, and additionally underscores the importance of individualized care and structured monitoring in real-world settings.
Keywords: Adherence; Cabotegravir (CAB); Efficacy; HIV treatment; Injectables; Long-acting (LA) HIV therapy; Real-world; Rilpivirine (RPV); Undetectable VL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of Interest: Olaf Degen was investigator in ViiV-sponsored clinical studies and acted as consulted for ViiV in the past. All other authors (Catharina Dannenberg, Hanna Matthews, Anja Hüfner, Gabriel Drewinski, Anna Koval, Sabine Jordan, Stefan Schmiedel, and Julian Schulze zur Wiesch) declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical Approval: This retrospective observational cohort study was conducted at the Outpatient Center of the Division of Infectious Diseases, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Germany. The study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Hamburg Medical Association (Ärztekammer Hamburg, reference no. PV6019). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was performed in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Long-Acting Injectable Agents for HIV-1: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023 Jul 27;9:e46767. doi: 10.2196/46767. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023. PMID: 37498645 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Suppression Rates at 48 Weeks in People With HIV Starting Long-Acting Cabotegravir/Rilpivirine With Initial Viremia.Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 30;80(4):864-870. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae500. Clin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39367871 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine in viraemic people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis.HIV Med. 2025 Jul;26(7):993-1003. doi: 10.1111/hiv.70025. Epub 2025 Apr 9. HIV Med. 2025. PMID: 40204512
-
Improving Adherence to the Target Window for Cabotegravir + Rilpivirine Long-Acting Injections Through the CHORUS™ App and Web Portal: A Cluster Randomized Trial.J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:23259582241245223. doi: 10.1177/23259582241245223. J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care. 2024. PMID: 38613372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of long-acting cabotegravir/rilpivirine for people with HIV and adherence challenges at the Ward 86 clinic: an intermediate outcome analysis.AIDS. 2025 Jun 1;39(7):899-904. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000004145. Epub 2025 Feb 4. AIDS. 2025. PMID: 39912762
References
-
- WHO. New WHO guidance on HIV viral suppression and scientific updates released at IAS 2023. 2023. https://www.who.int/news/item/23-07-2023-new-who-guidance-on-hiv-viral-s.... Accessed 10 Apr 2025.
-
- ViiV Healthcare announces the marketing authorisation of the first complete long-acting injectable HIV treatment in Europe. https://viivhealthcare.com/hiv-news-and-media/news/press-releases/2020/d.... Accessed 7 Dec 2024.
-
- CHMP. Vocabria, INN-cabotegravir. www.ema.europa.eu/contact. Accessed 12 Apr 2025.
-
- CHMP. ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS.
-
- Sax PE, Thompson MA, Saag MS. Updated treatment recommendation on use of cabotegravir and rilpivirine for people with HIV from the IAS-USA guidelines panel. JAMA. 2024;331:1060–1. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

