The WWP1-JARID1B axis sustains acute myeloid leukemia chemoresistance
- PMID: 40627385
- PMCID: PMC12280953
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2421159122
The WWP1-JARID1B axis sustains acute myeloid leukemia chemoresistance
Abstract
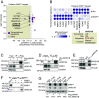
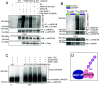
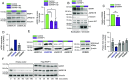
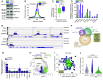
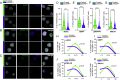
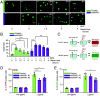
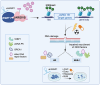
To uncover substrates mediating the oncogenic activity of WWP1 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), we performed a proteomic analysis that identified the histone demethylase KDM5B/JARID1B as a candidate target. Of note, JARID1B is indispensable for efficient recruitment of several DNA damage repair factors and for damage resolution, thus negatively influencing the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemo- and radiation therapies. Validation of JARID1B as a substrate of WWP1 revealed a positive regulation of JARID1B half-life by WWP1 through the establishment of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains. As a result, downregulation of JARID1B rising from WWP1 inactivation was associated with higher H3K4me3 enrichment at JARID1B target genes in WWP1-depleted relatively to control AML cells. Integration of RNA-seq and H3K4me3 ChIP-seq data uncovered a highly significant overlap between upregulated gene expression and enriched H3K4me3 peaks after shWWP1 inactivation. We confirmed transcriptional activation of JARID1B targets in WWP1-depleted cells, supporting a role for WWP1 in regulating JARID1B activity. Coherently, upon WWP1 inactivation, we observed a defective recruitment of repair proteins after DNA damage, with subsequent reduced DNA damage repair efficiency and enhanced sensitization of AML cells to the cytotoxic activity of chemotherapeutic drugs. All together, these data identify JARID1B as a bona fide target of WWP1 and imply that WWP1-mediated regulation of JARID1B impacts its ability to modify chromatin and to recruit DNA damage repair factors, thus ultimately affecting chemosensitivity of AML cells.
Keywords: DNA repair; acute myeloid leukemia; protein degradation; protein ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

