RP1 Combined With Nivolumab in Advanced Anti-PD-1-Failed Melanoma (IGNYTE)
- PMID: 40627813
- PMCID: PMC12622257
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-01346
RP1 Combined With Nivolumab in Advanced Anti-PD-1-Failed Melanoma (IGNYTE)
Abstract
Purpose: Effective treatment options for melanoma after immune checkpoint blockade failure are limited. RP1 (vusolimogene oderparepvec) is a herpes simplex virus type 1-based oncolytic immunotherapy, here evaluated in combination with nivolumab in anti-PD-1-failed melanoma.
Methods: Patients had advanced melanoma that had confirmed progression on anti-PD-1 (≥8 weeks, last prior treatment). RP1 was administered intratumorally (≤8 doses, ≤10 mL/dose; additional doses allowed) with nivolumab (≤2 years). The objective response rate (ORR) was assessed by independent central review using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1.
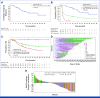
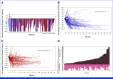
Results: Of 140 patients enrolled, 48.6% had stage IVM1b/c/d disease, 65.7% had primary anti-PD-1 resistance, 56.4% were PD-L1 negative, and 46.4% received prior anti-PD-1 and anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 therapy (43.6% in combination and 2.9% sequentially). Confirmed ORR (95% CI) was 32.9% (95% CI, 25.2% to 41.3%; 15.0% complete response). Responses occurred with similar frequency, depth, duration, and kinetics for injected and noninjected, including visceral lesions. The median (95% CI) duration of response was 33.7 (95% CI, 14.1 to not reached) months. Overall survival rates (95% CI) at 1 and 2 years were 75.3% (95% CI, 66.9% to 81.9%) and 63.3% (95% CI, 53.6% to 71.5%), respectively. Biomarker analysis demonstrated broad immune activation associated with response, including increased CD8+ T-cell infiltration and PD-L1 expression. Treatment-related adverse event rates were 77.1% grade 1/2, 9.3% grade 3, 3.6% grade 4, and no grade 5 events.
Conclusion: RP1 combined with nivolumab provided deep and durable systemic responses in patients with anti-PD-1-failed melanoma, including those with poor prognostic factors. The safety profile was favorable, with mostly grade 1/2 adverse events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03767348.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures

References
-
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1535–1546. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2521–2532. - PubMed
-
- Ribas A, Hamid O, Daud A, et al. Association of pembrolizumab with tumor response and survival among patients with advanced melanoma. JAMA. 2016;315:1600–1609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

