Effect of coated organic acids on growth performance, Clostridium perfringens colonization, gut integrity and immune response in broilers challenged with subclinical necrotic enteritis
- PMID: 40628145
- PMCID: PMC12272434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105504
Effect of coated organic acids on growth performance, Clostridium perfringens colonization, gut integrity and immune response in broilers challenged with subclinical necrotic enteritis
Abstract
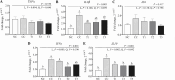
Necrotic enteritis (NE) is considered a major enteric disease that compromises intestinal health and causes significant economic losses in broiler production. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of dietary coated organic acids (COA) supplementation on growth, Clostridium perfringens colonization, gut integrity, and immune response in broilers challenged with NE. A total of 420 one-day-old broilers were allocated to 30 cages for 28 days. Five treatments included a non-challenged control and four NE-challenged groups with different dietary COA supplementation levels (0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 %). Birds in NE groups were challenged with Eimeria maxima on day 14 and C. perfringens on days 18 and 19. Major measurements included daily feed intake (FI); weekly body weight gain (BWG) and feed conversion ratio (FCR); intestinal C. perfringens load on days 20, 21, and 28; NE lesion score and gut permeability on days 20 and 21; and gene expression of tight junction proteins and cytokines in the jejunum on day 21. Results showed that increasing dietary COA dose-dependently improved FCR from day 0 to 14, with the lowest FCR observed at 0.1 % COA from day 7 to 14 (P < 0.05). Under NE, dietary COA linearly improved BWG and cumulative FI from day 14 to 28 and FCR from day 14 to 21 (P < 0.05). On day 21, dietary COA decreased intestinal C. perfringens loads, NE lesions, and gut permeability in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Additionally, dietary COA dose-dependently increased the expression of claudin-2 and zonula occludin-2 but decreased the expression of claudin-1, interleukin-1β, interferon-γ, and interleukin-10 (P < 0.05). These results indicate that dietary COA may improve early feed efficiency at a lower dose (0.1 %) and mitigate growth loss in NE-challenged broilers by reducing intestinal C. perfringens colonization and modulating gut integrity and immune responses in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, this study suggests that dietary COA could be a potential intervention to alleviate the adverse effects of NE and improve broiler productivity.
Keywords: Broiler; Coated organic acids; Gut health; Immune response; Necrotic enteritis.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures There is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Elucidating the Varying Impact of Necrotic Enteritis Using Performance and Health Indicators in Broiler Infection Models.Avian Dis. 2024 Jan;67(4):326-339. doi: 10.1637/aviandiseases-D-23-00048. Avian Dis. 2024. PMID: 38300654
-
Precision biotics enhance growth performance in broiler chickens by selectively modifying their intestinal microbiome to better respond to enteric challenges.Poult Sci. 2025 Sep;104(9):105454. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105454. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40544677 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of in ovo and water supplementation of a postbiotic on intestinal integrity and immune responses in broiler chickens challenged with necrotic enteritis.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Aug 13;12:1654028. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1654028. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40881634 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis probiotic in preventing necrotic enteritis in broilers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Avian Pathol. 2024 Dec;53(6):451-466. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2024.2359596. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Avian Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38776185
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd El-Ghany W.A. Applications of organic acids in poultry production: an updated and comprehensive review. Agriculture. 2024;14:1756.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

