Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces venous dysfunction via EPAS1 regulation in mice
- PMID: 40628749
- PMCID: PMC12238411
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61614-3
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces venous dysfunction via EPAS1 regulation in mice
Abstract
Vascular dementia is the second most common form of dementia. Yet, the mechanisms by which cerebrovascular damage progresses are insufficiently understood. Here, we create bilateral common carotid artery stenosis in mice, which effectively impairs blood flow to the brain, a major cause of the disease. Through imaging and single-cell transcriptomics of the mouse cortex, we uncover that blood vessel venous cells undergo maladaptive structural changes associated with increased Epas1 expression and activation of developmental angiogenic pathways. In a human cell model comparing arterial and venous cells, we observe that low-oxygen condition leads to sustained EPAS1 signaling specifically in venous cells. EPAS1 inhibition reduces cerebrovascular abnormalities, microglial activation, and improves markers of cerebral perfusion in vivo. In human subjects, levels of damaged endothelial cells from venous vessels are correlated with white matter injury in the brain and poorer cognitive functions. Together, these findings indicate EPAS1 as a potential therapeutic target to restore cerebrovascular integrity and mitigate neuroinflammation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
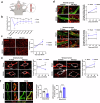


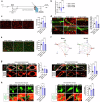

References
-
- Brown, W. R., Moody, D. M., Challa, V. R., Thore, C. R. & Anstrom, J. A. Venous collagenosis and arteriolar tortuosity in leukoaraiosis. J. Neurol. Sci.203-204, 159–163 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Quick, S., Moss, J., Rajani, R. M. & Williams, A. A vessel for change: endothelial dysfunction in cerebral small vessel disease. Trends Neurosci.44, 289–305 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Vanlandewijck et al. A molecular atlas of cell types and zonation in the brain vasculature. Nature554, 475–480 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Fischer, A., Zalvide, J., Faurobert, E., Albiges-Rizo, C. & Tournier-Lasserve, E. Cerebral cavernous malformations: from CCM genes to endothelial cell homeostasis. Trends Mol. Med.19, 302–308 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RGY0069/2019/Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP)
- MOE2017-T3-1-002, T2EP30122-0008, and RG88/21/Ministry of Education - Singapore (MOE)
- Core funding/Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory (TLL)
- Vascular Research Initiative/NTU | Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University (Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine)
- SP1CLNT900-NTU-A630-PJ-03INP001400A630/NTU | Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University (Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

