Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Critical Care Medicine: a consensus of 22
- PMID: 40629428
- PMCID: PMC12239397
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-025-05532-2
Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Critical Care Medicine: a consensus of 22
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of critical care, offering opportunities for enhanced diagnostic precision and personalized patient management. However, its integration into ICU clinical practice presents significant challenges related to equity, transparency, and the patient-clinician relationship. To address these concerns, a multidisciplinary team of experts was established to assess the current state and future trajectory of AI in critical care. This consensus identified key challenges and proposed actionable recommendations to guide AI implementation in this high-stakes field. Here we present a call to action for the critical care community, to bridge the gap between AI advancements and the need for humanized, patient-centred care. Our goal is to ensure a smooth transition to personalized medicine while, (1) maintaining equitable and unbiased decision-making, (2) fostering the development of a collaborative research network across ICUs, emergency departments, and operating rooms to promote data sharing and harmonization, and (3) addressing the necessary educational and regulatory shifts required for responsible AI deployment. AI integration into critical care demands coordinated efforts among clinicians, patients, industry leaders, and regulators to ensure patient safety and maximize societal benefit. The recommendations outlined here provide a foundation for the ethical and effective implementation of AI in critical care medicine.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Critical care medicine; Ethics; Healthcare innovation; Personalized medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors consent to this publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
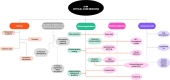
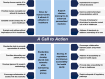

References
-
- Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019;25:44–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

