IGF2BP2 binding to CPSF6 facilitates m6A-mediated alternative polyadenylation of PUM2 and promotes malignant progression in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 40629911
- PMCID: PMC12238680
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.70388
IGF2BP2 binding to CPSF6 facilitates m6A-mediated alternative polyadenylation of PUM2 and promotes malignant progression in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and alternative polyadenylation (APA) are common posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in eukaryotes. However, the m6A-dependent mechanism of APA regulation in ovarian cancer (OC) is still unclear.
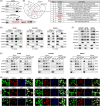
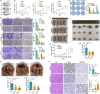
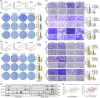
Methods: The correlation between m6A and APA was analyzed by using RNA methylation sequencing of OC cells and single-cell sequencing of clinical samples from public databases. To explore the core regulatory factors that served as a bridge between m6A and APA, we employed RNA pull-down with biotin-labelled m6A, immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry, western blot, protein purification and GST pull-down assays. Furthermore, the important target genes were screened by PAS-seq, eCLIP-seq, RIP-seq and meRIP-seq, and verified by RT-qPCR, 3'RACE, RNA stability, and dual luciferase reporter assays. Multiple phenotypic experiments were conducted to evaluate the function of the IGF2BP2-PUM2 axis in vitro and in vivo.
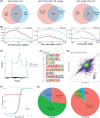
Results: This study found that the m6A was correlated with the APA and affected the 3'end processing in OC. The APA regulator CPSF6 tended to bind the m6A-modified transcripts in OC cells. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that the m6A reader IGF2BP2 KH1-4 domains could directly bind to the CPSF6-RS domain to regulate the 3'end processing of OC. Furthermore, sequencing revealed that the m6A was highly enriched in the 3'UTR near the proximal polyadenylation signal (PAS), which promotes the use of proximal PAS and leads to 3'UTR shortening. PUM2 was carried m6A and recognized by IGF2BP2, and CPSF6 was recruited at the proximal polyadenylation signal (pPAS) to generate the short-3'UTR transcript. The short PUM2 transcript was more stable than the long transcript, which promoted the malignant progression of OC.
Conclusions: We revealed a novel mechanism in which the m6A could regulate the APA processing of pre-mRNAs by crosstalk of IGF2BP2 and CPSF6. This study provides a potential strategy for the effective treatment of OC.
Highlights: The interaction between m6A and APA is mediated by the m6A regulator IGF2BP2 and the APA factor CPSF6. The transcripts harboring m6A modification tend to use the proximal polyadenylation signal (PAS) in ovarian cancer (OC). PUM2 promotes the malignant progression of OC through its m6A methylation and APA processing.
Keywords: CPSF6; IGF2BP2; N6‐methyladenosine; PUM2; alternative polyadenylation; ovarian cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CSTF3 contributes to platinum resistance in ovarian cancer through alternative polyadenylation of lncRNA NEAT1 and generating the short isoform NEAT1_1.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 19;15(6):432. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06816-1. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38898019 Free PMC article.
-
circFTO binding with IGF2BP2 regulates trophoblast cells proliferation, migration, and invasion while mediating m6A modification of CCAR1 mRNA in spontaneous abortion.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jul 2;26(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12860-025-00546-8. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40604397 Free PMC article.
-
IGF2BP2 alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells via m6A-dependent stabilization of LGI4 mRNA.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jul 14;163:115206. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115206. Online ahead of print. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40663812
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82172778/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CYB21197/Chongqing Graduate Research Innovation Project
- KY23039/Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
- W0058/CQMU Program for Youth Innovation in Future Medicine
- ZK202004/Program for Key Disciplines Construction from Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
