Comparative analysis of five obesity-related indicators for predicting infertility in U.S. adults
- PMID: 40630166
- PMCID: PMC12234334
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1593706
Comparative analysis of five obesity-related indicators for predicting infertility in U.S. adults
Abstract
Objective: Infertility is increasingly prevalent worldwide, emerging as a significant endocrine disorder of global concern. This study sought to explore associations between infertility and five distinct obesity-related metrics: body roundness index (BRI), relative fat mass (RFM), body mass index (BMI), lipid accumulation product (LAP), and waist circumference (WC). Evaluated and compared the predictive performance of these indicators in screening for infertility additionally.
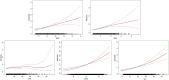
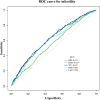
Methods: This research utilized data from the 2013-2018 cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Weighted logistic regression analyses with multi-model adjustments were performed to examine the relationship between five specific indicators and infertility. The diagnostic potential of five indicators was evaluated through receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC). Two part linear regression models are also used to estimate threshold effects. The association between the indicators and infertility was examined using smooth curve fitting techniques, while subgroup analyses were conducted to identify variations in risk across different population segments.
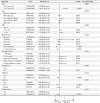
Results: The study included 3,528 participants from NHANES 2013-2018, comprising 365 individuals with infertility and 3,163 without. Weighted multivariate logistic regression analysis identified BRI, RFM, BMI, WC, and LAP as significant predictors of infertility. The odds ratios for the highest quartiles were 2.56 for BRI, 2.45 for RFM, 2.38 for BMI, 2.33 for WC, and 1.40 for LAP. Optimal thresholds were determined as 6.47 for BRI, 36.4 for BMI, 30.29 for RFM, 119.20 for WC, and 19.15 for LAP. The area under the ROC curve for BRI was 0.651, indicating moderate predictive performance. Subgroup analyses revealed that individuals aged over 35, smokers, and those with diabetes or hypertension were more likely to report infertility.
Conclusion: All five obesity-related indicators were positively associated with infertility in the U.S. population. Among them, BRI demonstrated relatively stronger predictive performance. Beyond the natural influence of aging, particular attention should be directed toward the prevention of smoking, diabetes, and hypertension to mitigate associated risks.
Keywords: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; body roundness index; lipid accumulation product; obesity-index; relative fat mass.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Zhao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer LY declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

