Analysis of the Clinical Symptom Improvement and Recurrence Rate in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media Patients Treated with Combination Therapy: Combination of Ofloxacin and Dexamethasone
- PMID: 40630217
- PMCID: PMC12236466
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S520505
Analysis of the Clinical Symptom Improvement and Recurrence Rate in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media Patients Treated with Combination Therapy: Combination of Ofloxacin and Dexamethasone
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the clinical symptom improvement and recurrence rate of chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) patients treated with a combination therapy regimen (combination of ofloxacin and dexamethasone).
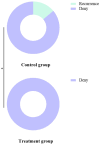
Methods: Based on the treatment regimen, patients were divided into two groups: the control group was treated with dexamethasone, while the treatment group received a combination of ofloxacin and dexamethasone. The clinical symptom improvement, hearing evaluation, pathogen clearance rate, inflammatory marker detection, adverse reactions, recurrence rate and recurrence rate post-treatment were compared between the two groups.
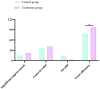
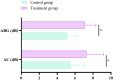
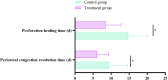
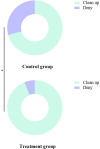
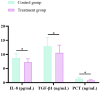
Results: There were no significant differences in the baseline clinical data between the two groups (P > 0.05). The overall clinical efficacy of the treatment group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, the improvements in air conduction (AC) and air-bone gap (ABG) in the treatment group were significantly greater than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The time for the resolution of tympanic membrane congestion and the healing of perforations was shorter in the treatment group compared to the control group (P < 0.05). The pathogen clearance rate in the treatment group was significantly higher than in the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, levels of inflammatory markers IL-8, TGF-β1, and PCT in the treatment group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The combination therapy of ofloxacin and dexamethasone significantly improves the clinical symptoms, reduces the recurrence rate, and lowers the incidence of adverse reactions in chronic suppurative otitis media patients. It shows significant clinical efficacy with improved hearing outcomes, and is worthy of clinical promotion. However, this study still has certain limitations, such as the possibility of introducing selection bias. In the future, prospective clinical trials with multiple centers and large samples can be conducted.
Keywords: chronic suppurative otitis media; clinical symptoms; dexamethasone; ofloxacin; recurrence rate; treatment effect.
© 2025 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Topical versus systemic antibiotics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013053. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013053.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484402
-
Aural toilet (ear cleaning) for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013057. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013057.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484404
-
Antibiotics versus topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013056. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013056.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484400
-
Topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013055. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013055.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484403
-
Topical antibiotics with steroids for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013054.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484406
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

