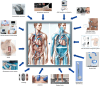
Application of Telemedicine in the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Focus on Heart Failure
- PMID: 40630466
- PMCID: PMC12230835
- DOI: 10.31083/RCM37835
Application of Telemedicine in the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Focus on Heart Failure
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that represents one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in developed nations. It is well established that every HF-related hospital admission leads to worsened quality of life for the patient and their caregiver and also imposes a significant financial burden on society. Therefore, reducing hospital admissions for this population has emerged as a critical tactic over the past decades. Initial attempts at remote monitoring focused on self-reported vital signs and symptoms, yet these proved ineffective. Meanwhile, subsequent technological advancements have enabled the development of miniature sensors capable of detecting and monitoring a wide range of physiologically relevant parameters; some of these advancements have been integrated into implantable devices, such as pacemakers and defibrillators. However, noninvasive monitoring has recently emerged as an alternative option for patients with HF, offering early congestion detection without requiring an invasive procedure. This review aims to summarize implanted and noninvasive devices, their characteristics, monitored parameters, and potential limitations and challenges around their integration into routine clinical practices.
Keywords: heart failure; noninvasive monitoring; remote heart failure management; telemedicine.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
TA serves as a consultant for Abbott, Inc and Edwards Life Sciences, Inc. TA serves on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott, Inc and Edwards Life Sciences, Inc. TA serves as site principal investigator for multiple clinical trials, including GUIDE-HF, PROACTIVE, and VICTOR. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (London, England) . 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giles L, Freeman C, Field P, Sörstadius E, Kartman B. Humanistic burden and economic impact of heart failure – a systematic review of the literature. F1000Research . 2019;8:859. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.19365.1. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous