This is a preprint.
Yellow Fever Virus Interactomes Reveal Common and Divergent Strategies of Replication and Evolution for Mosquito-borne Flaviviruses
- PMID: 40631121
- PMCID: PMC12236827
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.14.659623
Yellow Fever Virus Interactomes Reveal Common and Divergent Strategies of Replication and Evolution for Mosquito-borne Flaviviruses
Abstract
Pathogenic mosquito-borne flaviviruses infect mosquito and human hosts, relying on host protein interactions to replicate, evade immunity, and mediate pathogenesis. Prior proteomic studies mapped such interactions for some flaviviruses, but yellow fever virus (YFV)-a pathogen of resurgent concern-remains understudied. Here, we map YFV interactomes in human and mosquito cells to identify interactions common among divergent flaviviruses or unique to YFV. Functional assays reveal a previously unrecognized YFV restriction factor: RBBP6 inhibits YFV genome replication by interacting with the viral polymerase NS5. We enhance the identification of dual-host interactions using structural modeling and holistic network integration. Extending our holistic approach to other flavivirus interactomes, we distinguish conserved mechanisms of host targeting from those unique to YFV. Contrary to expectations that conserved viral proteins lead to conserved protein interactions, we find that Capsid, a divergent structural protein, shares more host interactions than NS5, a conserved enzyme. Integrating proteomics with complementary analyses defines new principles of host-targeting strategies across flavivirus and host evolution, offering a versatile resource for navigating the complex landscape of flavivirus biology.
Keywords: flaviviruses; integrative proteomics; systems biology; virus-host evolution; virus-host interaction; yellow fever virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests All authors report no competing interests.
Figures

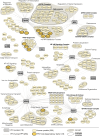

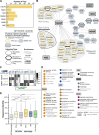
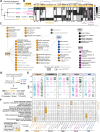

References
-
- Kolimenakis A., Heinz S., Wilson M.L., Winkler V., Yakob L., Michaelakis A., Papachristos D., Richardson C., and Horstick O. (2021). The role of urbanisation in the spread of Aedes mosquitoes and the diseases they transmit—A systematic review. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 15, e0009631. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009631. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
