The Relationships of Early Use of Marijuana With Substance Use and Violence in Adolescent Gamblers and Non-Gamblers
- PMID: 40631639
- PMCID: PMC12223671
- DOI: 10.5765/jkacap.250012
The Relationships of Early Use of Marijuana With Substance Use and Violence in Adolescent Gamblers and Non-Gamblers
Abstract
Objectives: Marijuana use (MU) and gambling are prevalent among adolescents, and marijuana products are becoming increasingly available and normalized globally. This study explored the relationships between early- (age <13 years), later- (age ≥13 years), and no-MU and substance use and violence among adolescents who gambled and did not gamble.
Methods: It analyzed data from the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance survey (n=2015) on MU, gambling, demographics, substance use, and violence, using adjusted multivariate logistic regression models.
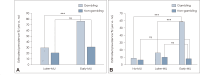
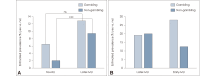
Results: The odds of current cigarette smoking, alcohol use, and heavy alcohol use; lifetime use of any substance and cocaine; current and lifetime electronic vapor product use; and physical fighting were higher across adolescents with early and later MU than those with no MU. Gambling adolescents with early-MU, compared to later- and no-MU, respectively, had greater odds of any substance use and prescription opiate misuse. Non-gambling adolescents with later-MU had higher odds of having experienced forced sexual intercourse than those with no-MU. MU by gambling status interactions were identified for prescription opiate misuse and any substance use, and having experienced bullying at school and forced sexual intercourse. However, while the simple main effects of MU on the odds of experiencing bullying among gamblers was approximately 3.9 times greater than that among non-gamblers, they were not statistically significant in either gambling group.
Conclusion: Early MU is associated with risky behaviors involving the use of other substances and violence, and its relationships with several factors differ according to gambling status. Reducing early engagement in addictive behaviors may be important for preventions against substance use disorders and interpersonal violence.
Keywords: Addictive behaviors; Adolescents; Gambling; Marijuana use; Violence.
Copyright © 2025 Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Incentives for preventing smoking in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD008645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008645.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28585288 Free PMC article.
-
Brief school-based interventions and behavioural outcomes for substance-using adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 20;2016(1):CD008969. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008969.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26787125 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological therapies for post-traumatic stress disorder and comorbid substance use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 4;4(4):CD010204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27040448 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19 who are using hormonal contraception.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 9;1(1):CD014908. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014908.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 15;5:CD014908. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014908.pub3. PMID: 36622724 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
