Microglial BDNF modulates arketamine's antidepressant-like effects through cortico-accumbal pathways
- PMID: 40632846
- PMCID: PMC12239974
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv5986
Microglial BDNF modulates arketamine's antidepressant-like effects through cortico-accumbal pathways
Abstract
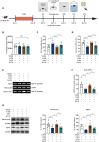
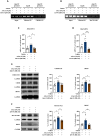
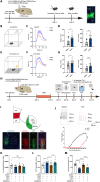
Arketamine, the (R)-enantiomer of (R,S)-ketamine, shows even greater rapid and sustained antidepressant-like effects in rodent models compared to esketamine, yet the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we used the chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) model to investigate how arketamine exerts its antidepressant-like effects. We found that activating cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) at S133 and methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) at S421 drives the transcription of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), contributing to arketamine's antidepressant-like effects. Furthermore, microglia-derived BDNF enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in the infralimbic (IL) region of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), mediating the antidepressant-like effects of arketamine in CSDS-susceptible mice. Last, microglia-derived BDNF can activate mPFC (IL) neurons projecting to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell, contributing to arketamine's antidepressant-like effects. These findings highlight the essential role of microglial BDNF in modulating NAc-projecting mPFC neurons, which contribute to the antidepressant-like effects of arketamine.
Figures






References
-
- Berman R. M., Cappiello A., Anand A., Oren D. A., Heninger G. R., Charney D. S., Krystal J. H., Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol. Psychiatry 47, 351–354 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson S. T., Ballard E. D., Bloch M. H., Mathew S. J., Murrough J. W., Feder A., Sos P., Wang G., Zarate C. A. Jr., Sanacora G., The effect of a single dose of intravenous ketamine on suicidal ideation: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 175, 150–158 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zarate C. A. Jr., Singh J. B., Carlson P. J., Brutsche N. E., Ameli R., Luckenbaugh D. A., Charney D. S., Manji H. K., A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 63, 856–864 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Zhang J. C., Yao W., Hashimoto K., Arketamine, a new rapid-acting antidepressant: A historical review and future directions. Neuropharmacology 218, 109219 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto K., Molecular mechanisms of the rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 177, 113935 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

