The effect of Lupinus angustifolius supplementation in laying hens on the liver proteome profiles and the concentration of acute phase proteins in serum and liver
- PMID: 40633312
- PMCID: PMC12275114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105507
The effect of Lupinus angustifolius supplementation in laying hens on the liver proteome profiles and the concentration of acute phase proteins in serum and liver
Abstract
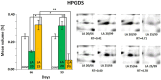
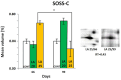
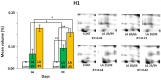
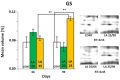
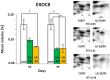
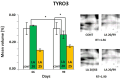
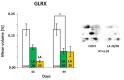
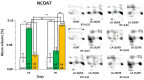
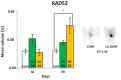
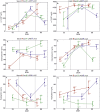
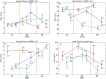
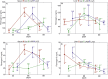
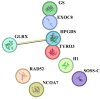
In the search for alternative protein sources for laying hens that meet production criteria and are an alternative to soybean meal, increasing attention is being paid to the lupine seeds which have high content of proteins, essential amino acids and low content of starch and low glycaemic index. Furthermore, the effect of lupin seed supplementation to the diet of laying hens on liver protein expression and acute phase protein synthesis has not yet been determined. The aim of the study was to identify proteins synthesized in the liver of laying hens fed a diet with a high content of Lupinus angustifolius (20 % and 25 %), to determine differences in their expression, and to evaluate the concentration of acute phase proteins in serum and liver of laying hens. The obtained results indicate that supplementation of lupin at a dose of 20 % and 25 % increases the expression of proteins such as hematopoietic prostaglandin-D synthetase, SOSS complex subunit C, DNA repair protein RAD25 homolog and basic histone H1 protein in the liver, with statistically significant differences being particularly visible in the case of a dose of 25 % lupin on day 99 of the study. Moreover, the use of high doses of lupin in the diet of hens, containing various bioactive substances, caused changes in the concentration of acute phase proteins in the liver, and especially an increase in the synthesis of serum amyloid A component and haptoglobin, which may also affect the synthesis and expression of other proteins in the body, including the liver.
Keywords: Acute phase proteins; Laying hens; Lupinus angustifolius, Liver proteomics; MALDI-TOF MS.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Citrullinemia Type I.2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301631 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Functional Feed for Laying Hens: Application of Saffron Extract as Eco-Friendly Supplement With Cholesterol-Lowering Properties.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Jan;11(1):e70155. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70155. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39642059 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary compounded traditional Chinese medicine residue meal improves laying performance, egg quality, and gut barrier integrity in late-phase laying hens.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun 11;104(9):105425. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105425. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40570464 Free PMC article.
-
Mental Health First Aid as a tool for improving mental health and well-being.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 22;8(8):CD013127. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013127.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37606172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bryden W.L., Li X.., Ruhnke I., Zhang D., Shini S. Nutrition, feeding and laying hen welfare. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2021;61:893–914. doi: 10.1071/AN20396. - DOI
-
- Chen L.R., Lee S..C., Lin Y.P., Hsieh Y.L., Chen Y.L., Yang J.R., Liou J.F., Chen C.F., Lee Y.P., Shiue Y.L. Prostaglandin-D synthetase induces transcription of the LH beta subunit in the primary culture of chicken anterior pituitary cells via the PPAR signaling pathway. Theriogenology. 2010;73:367–382. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2009.09.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

