Identification of Direct-Acting nsP2 Helicase Inhibitors with Antialphaviral Activity
- PMID: 40634283
- PMCID: PMC12305492
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00635
Identification of Direct-Acting nsP2 Helicase Inhibitors with Antialphaviral Activity
Abstract
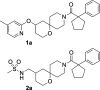
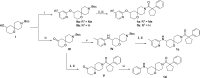
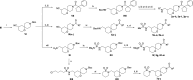
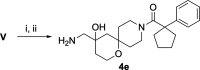
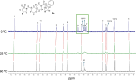
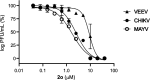
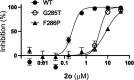
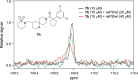
Alphaviruses are mosquito-borne RNA viruses that pose a significant public health threat, with no FDA-approved antiviral therapeutics available. The nonstructural protein 2 helicase (nsP2hel) is an enzyme involved in unwinding dsRNA essential for alphavirus replication. This study reports the discovery and optimization of first-in-class oxaspiropiperidine inhibitors targeting nsP2hel. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies identified potent cyclic sulfonamide analogs with nanomolar antiviral activity against chikungunya virus (CHIKV). Biochemical analyses of nsP2hel ATPase and RNA unwindase activities showed these compounds act in a noncompetitive mode, suggesting that they are allosteric inhibitors. Viral resistance mutations mapped to nsP2hel and a fluorine-labeled analog exhibited direct binding to the protein by 19F NMR. The lead inhibitor, 2o, demonstrated broad-spectrum antialphaviral activity, reducing titers of CHIKV, Mayaro virus (MAYV), and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV). These findings support nsP2hel as a viable target for the development of broad-spectrum, direct-acting antialphaviral drugs.
Figures



References
-
- Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Massachusetts arbovirus update. 2024. https://www.mass.gov/info-details/massachusetts-arbovirus-update (accessed 2024 September 1st).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

