Early-life exercise extends healthspan but not lifespan in mice
- PMID: 40634291
- PMCID: PMC12241455
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61443-4
Early-life exercise extends healthspan but not lifespan in mice
Abstract
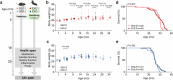
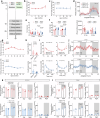
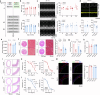
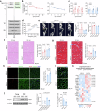
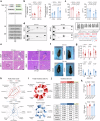
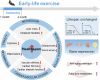
It is well-known that physical activity exerts health benefits, yet the potential impacts of early-life regular exercise on later-life health and lifespan remains poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that 3 months of early-life exercise in mice results in lasting health benefits, extending healthspan, but not lifespan. C57BL/6J mice underwent swimming exercise from 1 to 4 months of age, followed by detraining for the remainder of their lives. While early-life exercise did not extend the overall lifespan, it significantly improved healthspan in both male and female mice, as evidenced by enhanced systemic metabolism, cardiovascular function, and muscle strength, as well as reduced systemic inflammation and frailty in aged mice. Multiple-organ transcriptome analyses identified enhanced fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscles as a major feature in aged mice that underwent early-life exercise. These findings reveal the enduring long-term health benefits of early-life exercise, highlighting its pivotal role in improving healthspan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Global status report on physical activity 2022. (World Health Organization, 2022).
-
- Kohl, H. W. et al. The pandemic of physical inactivity: global action for public health. Lancet380, 294–305 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, X. & Gao, F. Exercise improves vascular health: role of mitochondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med177, 347–359 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

