Triggering AHR resolves TGF-β1 induced fibroblast activation and promotes AT1 cell regeneration in alveolar organoids
- PMID: 40634525
- PMCID: PMC12241620
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08446-5
Triggering AHR resolves TGF-β1 induced fibroblast activation and promotes AT1 cell regeneration in alveolar organoids
Abstract
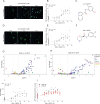
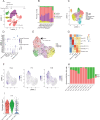
Regeneration of the alveolar epithelium is necessary to restore tissue architecture and gas exchange capabilities in chronic pulmonary diseases such as fibrosing interstitial lung disease. While it is known alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells give rise to alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells to repair the alveolar epithelium after injury, methods to promote this process under pathological settings are poorly understood. Here, using a complex 3D organoid culture with TGF-β1 dependent impaired AT1 spheroid formation, we performed a high-throughput screen (HTS) with ~16,800 compounds to identify small molecules that increase number of AT1 spheroids. Longitudinal single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) revealed that DB-11-BE87 increased AT1 regeneration by reducing TGF-β1 induced fibroblast activation, concurrently with AHR activation in those cells. These studies highlight a HTS system to identify factors that can promote AT1 differentiation and suggest AHR activation as a method to counteract pathological TGF-β1 signaling in pulmonary disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following competing interests: All authors are current or former employees and shareholders of Novartis.
Figures





References
-
- Crapo, J. D., Barry, B. E., Gehr, P., Bachofen, M. & Weibel, E. R. Cell number and cell characteristics of the normal human lung. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.126, 332–337 (1982). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

