The impact of serum neuregulin 4 (NRG-4) levels on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40634833
- PMCID: PMC12239356
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-04097-2
The impact of serum neuregulin 4 (NRG-4) levels on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the association between serum neuregulin 4 (Nrg4) levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
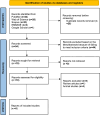
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed across Web of Science, EMBASE, Medline (PubMed), and Scopus to find all original published works in NAFLD up to March 2024. Studies were limited to case-control observational studies on humans. After removing duplicated studies, studies were screened based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The Joanna Briggs Institute checklist (JBI) was used for assessing the quality of case-control studies. The strength of the relationship was assessed by the odds ratios (ORs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All statistical analyses were performed using Stata 17.0.
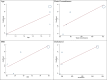
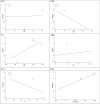
Results: Five case-control articles with 323 cases and 308 controls were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled mean ages were 42.6 years for the NAFLD group and 38.0 years for the control group. The pooled estimated OR between Nrg4 and NAFLD was 0.72 (95% CI: 0.67-0.77). The analysis shows that with increasing age (B: 1.381; SE: 0.732; P-value: 0.200; 95% CI: 0.771, 4.534), waist circumference (B: 0.076; SE: 0.041; P-value: 0.207; 95% CI: 0.002, 0.256) and TG levels (B: 0.0426; SE: 0.023; P-value: 0.212; 95% CI: -0.058, 0.143), the association of the Nrg4 index with incident NAFLD increased. Furthermore, the strength of the association between the Nrg4 index and incident NAFLD decreased with increasing levels of ALT (B: -0.124; SE: 0.119; P-value: 0.407; 95% CI: -0.638, 0.389) and HDL (B: -0.221; SE: 0.130; P-value: 0.232; 95% CI: -0.783, 0.340).
Conclusion: In summary, the findings from this meta-analysis strongly suggest that Nrg4 exerts a protective effect against the development of NAFLD. The evidence indicates that measuring Nrg4 levels holds significant promise for facilitating the early diagnosis and prognostication of NAFLD. However, it's essential to note that further research with larger sample sizes and more accurate study designs is needed to corroborate these findings and establish the clinical utility of Nrg4 as a biomarker in the management of NAFLD.
Keywords: Adipokine; Biomarker; Neuregulin 4; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval was not required for this study, as it is a meta-analysis and did not involve the collection of primary data. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Statins for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 27;2013(12):CD008623. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008623.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24374462 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplementation for nonalcohol-related fatty liver disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 19;7(7):CD013157. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013157.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34280304 Free PMC article.
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Liver Diseases: NAFLD, NASH, Fibrosis, Cirrhosis-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 9;14(24):5261. doi: 10.3390/nu14245261. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558421 Free PMC article.
-
Low circulating levels of neuregulin 4 as a potential biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of obesity-related metabolic diseases: a systematic review.Adipocyte. 2024 Dec;13(1):2390833. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2024.2390833. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Adipocyte. 2024. PMID: 39162358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amini-Salehi E, Letafatkar N, Norouzi N, Joukar F, Habibi A, Javid M, et al. Global Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Updated Review Meta-Analysis comprising a Population of 78 million from 38 Countries. Arch Med Res. 2024;55(6):103043. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2024.103043. PMID: 39094335. - PubMed
-
- Demir M, Lang S, Steffen HM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - current status and future directions. J Dig Dis. 2015;16(10):541–57. 10.1111/1751-2980.12291. PMID: 26406351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

