Liver-specific expression of ANGPTL8 promotes Alzheimer's disease progression through activating microglial pyroptosis
- PMID: 40634935
- PMCID: PMC12243332
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03487-3
Liver-specific expression of ANGPTL8 promotes Alzheimer's disease progression through activating microglial pyroptosis
Abstract
Introduction: Liver dysfunction contributes to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis, and evidence suggests that the liver is involved in amyloid β (Aβ) clearance, and regulates Aβ deposition in the brain. However, the specific regulatory mechanism remains elusive.
Objectives: Angiopoietin-like protein 8 (ANGPTL8), a high expression of liver-specific secreted proinflammatory factor, crosses the blood‒brain barrier from the bloodstream to abnormally activate microglia and promote AD progression.
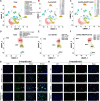
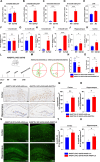
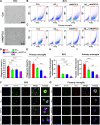
Methods: The ANGPTL8-/- mice and 5 × FAD mice were crossed mutated and subjected to the Morris water maze test and novel object recognition test to assess cognitive ability in different cohorts. Thioflavin-S, NeuN, and Nissl staining were used to assess Aβ deposition and neuron loss. The number of phagocytic microglia was evaluated with Fitc latex beads. Adeno-associated virus 8 (AAV8) hydrodynamically injected restored the liver ANGPTL8 levels of ANGPTL8-/- 5 × FAD mice for further experiments. Single-cell RNA sequencing, bulk RNA sequencing and transmission electron microscopy were used to explore the role of ANGPTL8 in regulating AD progression, and drug screening was carried out to identify an effective inhibitor of ANGPTL8.
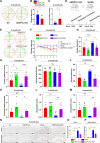
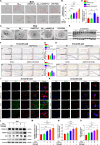
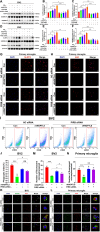
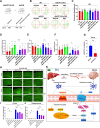
Results: ANGPTL8 knockout improved cognitive function and reduced Aβ deposition by reducing microgliosis and microglial activation in 5xFAD mice. Mechanistically, ANGPTL8 crossed the blood‒brain barrier and interacted with the microglial membrane receptor PirB/LILRB2. This interaction subsequently activated the downstream NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to microglial pyroptosis and exacerbating the Aβ-induced release of inflammatory factors, thereby accelerating AD progression. Furthermore, the administration of metformin, an ANGPTL8 inhibitor, improved learning and memory deficits in 5 × FAD mice by negating microglial pyroptosis and neuroinflammation.
Conclusions: ANGPTL8 aggravates microglial pyroptosis via the PirB/NLRP3 pathway to accelerate the pathogenesis of AD. Targeting high expression of ANGPTL8 in the liver may hold potential for developing therapies for AD.
Keywords: ANGPTL8; Alzheimer's disease; Liver‒brain axis; Microglial pyroptosis; Neuroinflammation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All experiments involving animals were conducted according to ethical policies and procedures approved by the ethics committee of Hubei University of Medicine, China. The ethical committee number for the study was 202016. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Porsteinsson AP, Isaacson RS, Knox S, Sabbagh MN, Rubino I. Diagnosis of Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Practice in 2021. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2021;8:371–86. - PubMed
-
- Moonen S, Koper MJ, Van Schoor E, Schaeverbeke JM, Vandenberghe R, von Arnim CAF, Tousseyn T, De Strooper B, Thal DR. Pyroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: cell type-specific activation in microglia, astrocytes and neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;145:175–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

