Transurethral Sphincterotomy and an Artificial Urinary Sphincter - A Novel 2-Stage Surgery for Refractory Bladder Emptying Disorders: A Proof-of-Concept Study
- PMID: 40635422
- PMCID: PMC12242176
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2550016.008
Transurethral Sphincterotomy and an Artificial Urinary Sphincter - A Novel 2-Stage Surgery for Refractory Bladder Emptying Disorders: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
Purpose: We developed an innovative 2-stage procedure combining transurethral sphincterotomy (TURS) with artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) implantation to restore voiding in patients with refractory bladder emptying disorders. This proof-of-concept study evaluated its safety and efficacy.
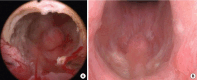
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed clinical data from patients who underwent combined TURS and AUS implantation between April 7, 2021, and October 31, 2024. Eligible patients had neurogenic bladder with refractory emptying, irreversible neurogenic disease, and no mechanical obstruction (e.g., urethral strictures). In the TURS stage, the entire inner urethral segment corresponding to the external sphincter was resected to induce intrinsic sphincter deficiency; this was followed by AUS placement. We analyzed patient demographics, preoperative and postoperative daily pad usage, clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) frequency, patient-reported outcomes (Life Quality [LQ], International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire [ICIQ], Sandvik Severity Index [SAND]), postvoid residual (PVR) urine volume, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), abdominopelvic ultrasonography, and postoperative complications.
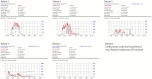
Results: Four out of 6 patients (66.7%) successfully achieved CIC-free status, with effective self-voiding achieved through AUS activation and abdominal pressure generation. Significant improvements were documented in LQ scores (P=0.042), ICIQ scores (P=0.004), and SAND scores (P=0.039). Median PVR significantly decreased from 237.5 mL (interquartile range [IQR], 112.5-317.5 mL) preoperatively to 1.5 mL (IQR, 0-85.8 mL) postoperatively (P=0.028). No patient demonstrated upper-tract damage or significant eGFR change. One patient developed an AUS infection requiring explantation; another remained CIC-dependent due to insufficient abdominal pressure.
Conclusion: Combining TURS with AUS implantation is a safe and effective surgical option for refractory bladder emptying disorders, yielding significant improvements in voiding autonomy and quality of life while reducing catheter dependence. Future studies with larger cohorts and longer follow-up are warranted to validate safety, long-term durability, and broader applicability. These findings may shift current paradigms in neurogenic bladder management.
Keywords: Intermittent urethral catheterization; Urinary bladder, Neurogenic; Urinary sphincter, Artificial.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Lapides J, Diokno AC, Silber SJ, Lowe BS. Clean, intermittent self-catheterization in the treatment of urinary tract disease. J Urol. 1972;107:458–61. - PubMed
-
- Lamin E, Newman DK. Clean intermittent catheterization revisited. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016;48:931–9. - PubMed
-
- Newman DK, New PW, Heriseanu R, Petronis S, Håkansson J, Håkansson M, et al. Intermittent catheterization with single- or multiple-reuse catheters: clinical study on safety and impact on quality of life. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020;52:1443–51. - PubMed
-
- Newman DK, Willson MM. Review of intermittent catheterization and current best practices. Urol Nurs. 2011;31:12–28. 48; quiz 29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

