Improving Soybean Seed Sucrose Content using TILLING by Sequencing Analyses of The Soybean Sucrose Synthase Gene Family
- PMID: 40636009
- PMCID: PMC12239747
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1606321
Improving Soybean Seed Sucrose Content using TILLING by Sequencing Analyses of The Soybean Sucrose Synthase Gene Family
Abstract
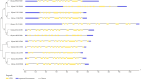
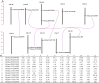
Soybean seed quality is influenced by its soluble sugar composition, with high sucrose content being desirable for nutritional and industrial applications. In contrast, excessive raffinose and stachyose levels are considered undesirable due to their adverse effects on gastrointestinal function in humans and monogastric animals. Therefore, developing soybean mutant lines with elevated sucrose content and optimal raffinose and stachyose content is desirable. In this study, we characterized twelve sucrose synthase genes through a comprehensive phylogenetic tree analysis, synteny analysis, gene structure evaluation, and variations in conserved domains. Additionally, we conducted a TILLING by Sequencing approach to identify EMS mutations in the characterized Sucrose synthase genes. Numerous mutations have been identified in soybean sucrose synthases that resulted in high sucrose content, including the sucrose synthases mutants SL446 (R582W) and F1115 (G249E) on Glyma.02G240400 with a sucrose content of 9.5% and 9.1%, respectively. The obtained soybean mutants with enhanced sugar content can be useful in breeding programs to improve soybean nutritional quality without potential developmental trade-offs.
Keywords: EMS mutagenesis; TILLING; glycine max; raffinose; soybean; stachyose; sucrose; sucrose synthase gene family.
Copyright © 2025 Knizia, Anil, Salhi, Shi, El Baze, Kassem, Lakhssassi, Nguyen and Meksem.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Andrews S. (2010). FastaQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
-
- AlbersCornelis A., DePristoMark A., HandsakerRobert E., MarthGabor T., SherryStephen T. (2011). The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

