c-Abl Inhibitors in Parkinson's: Exploring Hypotheses on Alpha-Synuclein Modulation
- PMID: 40636304
- PMCID: PMC12235367
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.42806
c-Abl Inhibitors in Parkinson's: Exploring Hypotheses on Alpha-Synuclein Modulation
Abstract
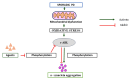
Parkinson's disease (PD) stands as the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, impacting a global population estimated between 6 to 10 million individuals. The condition primarily arises from a dopamine deficiency and the presence of α-synuclein, forming Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNcp). Despite the ongoing quest to unravel the precise pathophysiological mechanisms underlying PD, recent literature reviews posit that heightened activation of the Abelson non-receptor tyrosine kinase(c-Abl), in brain tissues plays a pivotal role in neurodegeneration observed in PD patients. Notably, these studies put forth compelling evidence suggesting that c-Abl inhibitors' interventions exhibit notable therapeutic potential. The potential benefits encompass enhancements in motor function, prevention of dopamine neuron loss, and the meticulous regulation of α-synuclein phosphorylation and clearance. These findings collectively advocate for the exploration of c-Abl as a prospective therapeutic target, thereby presenting inhibitors of this kinase as promising candidates for intervention in the management of PD.
Keywords: Neurodegeneration; Parkinson’s disease; Phosphorylation; c-Abl; α-synuclein.
© 2025 The Author (s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Tissue Factor and Its Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein Profiles in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(7):1405-1416. doi: 10.3233/JPD-240115. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39240648 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced alpha-synuclein pathology and exacerbated motor dysfunction in alpha-synuclein transgenic mice with autophagy deficiency.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Apr 12;758:151514. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151514. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40112535
-
Brain-derived extracellular vesicles: A promising avenue for Parkinson's disease pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Apr 1;21(4):1447-1467. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01262. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40313118
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors for dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease dementia and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Mar 14;2012(3):CD006504. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006504.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22419314 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the Proteinopathic Engagement of α-Synuclein, Tau, and Amyloid Beta in Parkinson's Disease: Mitochondrial Collapse as a Pivotal Driver of Neurodegeneration.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 16;50(3):145. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04399-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40240583 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous