Evaluation and comparison of large language models' responses to questions related optic neuritis
- PMID: 40636386
- PMCID: PMC12238082
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1516442
Evaluation and comparison of large language models' responses to questions related optic neuritis
Abstract
Objectives: Large language models (LLMs) show promise as clinical consultation tools and may assist optic neuritis patients, though research on their performance in this area is limited. Our study aims to assess and compare the performance of four commonly used LLM-Chatbots-Claude-2, ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.0, and Google Bard-in addressing questions related to optic neuritis.
Methods: We curated 24 optic neuritis-related questions and had three ophthalmologists rate the responses on two three-point scales for accuracy and comprehensiveness. We also assessed readability using four scales. The final results showed performance differences among the four LLM-Chatbots.
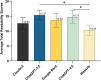
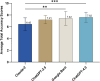
Results: The average total accuracy scores (out of 9): ChatGPT-4.0 (7.62 ± 0.86), Google Bard (7.42 ± 1.20), ChatGPT-3.5 (7.21 ± 0.70), Claude-2 (6.44 ± 1.07). ChatGPT-4.0 (p = 0.0006) and Google Bard (p = 0.0015) were significantly more accurate than Claude-2. Also, 62.5% of ChatGPT-4.0's responses were rated "Excellent," followed by 58.3% for Google Bard, both higher than Claude-2's 29.2% (all p ≤ 0.042) and ChatGPT-3.5's 41.7%. Both Claude-2 and Google Bard had 8.3% "Deficient" responses. The comprehensiveness scores were similar among the four LLMs (p = 0.1531). Note that all responses require at least a university-level reading proficiency.
Conclusion: Large language models-Chatbots hold immense potential as clinical consultation tools for optic neuritis, but they require further refinement and proper evaluation strategies before deployment to ensure reliable and accurate performance.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; eye diseases; natural language processing; optic nerve diseases; optic neuritis.
Copyright © 2025 He, Zhao, Liang, Wang, He, Lin, Cen, Chen, Li, Hu, Yang, Chen, Cheung, Tham and Cen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- OpenAI. Introducing ChatGPT. (2024). Available online at: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed April 16, 2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

