Revealing the Catalytic Strategy of FTO
- PMID: 40636456
- PMCID: PMC12240458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.checat.2023.100732
Revealing the Catalytic Strategy of FTO
Abstract
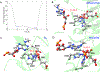
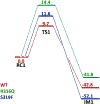
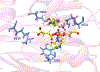
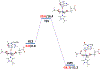
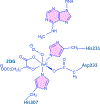
The fat-mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) is a Fe(II) and 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent oxygenase of the AlkB family and is linked with obesity and cancer. The enzyme is identified as single-stranded DNA/RNA demethylase with N6-methyladenine (m6A) modification in RNA as its most favorable substrate. Herein we used Molecular Dynamics (MD), metadynamics (MetD), and hybrid Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) calculations to reveal the catalytic mechanism of FTO with pentanucleotide-ssRNA(m6A) substrate and elucidate the effects of clinically significant mutations R316Q and S319F. The calculations explored the catalytic mechanism of the O2 activation and substrate oxidation in the WT FTO, revealing that different networks of residues stabilize the TSs of the different reaction steps. The mutations influence the interactions in the jelly-roll motif and loops in FTO and in particular, S319F strongly affects the substrate binding. The R316Q mutant slows down the O2 activation and HAT rates in agreement with experimental studies.
Keywords: Catalysis; FTO; Molecular dynamics; Non-heme enzyme; Quantum Mechanics/ Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM); conformational study; mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

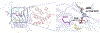
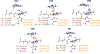
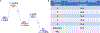

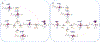


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
