Whole-genome sequencing shows modulation of neurodegenerative genes by Withania somnifera in human SK-N-SH cells
- PMID: 40636521
- PMCID: PMC12238756
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1512727
Whole-genome sequencing shows modulation of neurodegenerative genes by Withania somnifera in human SK-N-SH cells
Abstract
Background: Aging is driven by several primary and secondary hallmarks that manifest with age, of which neurodegenerative diseases are important manifestations. The ability to decelerate or reverse aging, and promote healthy aging, has garnered great interest in recent times. In traditional medicine, Withania somnifera (WS) or Ashwagandha has been recognized for its adaptogenic and rejuvenative effects.
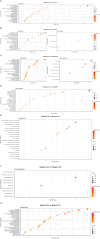
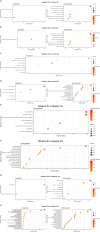
Methods: To investigate WS-modulated global gene expression profiles, we performed whole-genome sequencing of WS-treated human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells at different doses (50 and 100 μg/mL) and time points (3 h and 9 h) and validation by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunoblotting. Disease enrichment analysis for brain-related disorders was performed by DisGeNET.
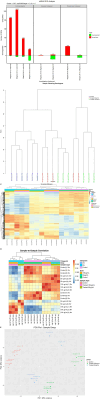
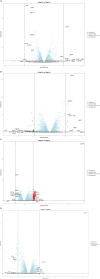
Results: Using differential gene expression analyses, we identified 19,945 WS-modulated genes. Of these, 2,403 and 177 genes were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) upregulated and downregulated, respectively, by WS treatment. Interestingly, different patterns of gene expression were exhibited in dose-dependent (9 upregulated, 1 downregulated, 100 μg/mL 3 h vs. 50 μg/mL 3 h; 21 upregulated, 86 downregulated, 100 μg/mL 9 h vs. 50 μg/mL 9 h) and temporal kinetics (210 upregulated, 6 downregulated, 50 μg/mL 9 h vs. 50 μg/mL 3 h; 8 upregulated, 49 downregulated, 100 μg/mL 9 h vs. 100 μg/mL 3 h). Furthermore, qRT-PCR experiments validated the RNA-seq results. WS-modulated genes were implicated in Alzheimer's disease, migraine, Parkinson's disease, bipolar disorder, cognition, stress, anxiety, forgetfulness, sleep disorders, and substance abuse among others.
Conclusion: Taken together, our transcriptomic profiling study revealed for the first time that WS may modulate key genes in neurodegenerative disorders with potential beneficial implications for brain-related disorders and healthy aging.
Keywords: Withania somnifera; aging; ashwagandha; healthy aging; neurodegenerative disease; whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 Sharma, Mehta, Jadhav, Gujrati, Dhananya, Moorthy, Ramaswamy, Zhou and Nair.
Conflict of interest statement
ES, DM, GG, and SN are employees of Phytoveda Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India and Viridis Biopharma Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Atluri V. S. R., Tiwari S., Rodriguez M., Kaushik A., Yndart A., Kolishetti N., et al. (2020). Inhibition of amyloid-Beta production, associated Neuroinflammation, and histone deacetylase 2-mediated epigenetic modifications prevent neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease in vitro model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:342. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00342, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barve A., Khor T. O., Nair S., Lin W., Yu S., Jain M. R., et al. (2008). Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and drug metabolism: pharmacogenomic profile of soy isoflavone concentrate in the prostate of Nrf2 deficient and wild-type mice. J. Pharm. Sci. 97, 4528–4545. doi: 10.1002/jps.21311 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

