Targeting alveolar epithelial cell metabolism in pulmonary fibrosis: Pioneering an emerging therapeutic strategy
- PMID: 40636669
- PMCID: PMC12238887
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1608750
Targeting alveolar epithelial cell metabolism in pulmonary fibrosis: Pioneering an emerging therapeutic strategy
Abstract
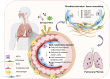
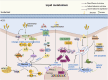
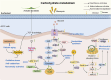
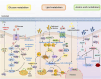
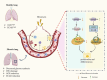
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic and progressive lung disease, characterized by excessive deposition of fibrotic connective tissue within the lungs. Advances in transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics have enhanced our understanding of PF's pathogenesis. Recent studies have indicates that metabolic abnormalities in alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) play a central role in the pathogenesis of PF. Metabolic reprogramming of AECs affects cellular senescence, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and oxidative stress in AECs, while also promoting fibrotic progression through various signaling pathways. This review focuses on therapeutic strategies targeting the metabolism of AECs. It comprehensively explores the role of metabolic pathways through glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism in the pathogenesis of PF, aiming to provide novel theoretical support and research perspectives for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: alveolar epithelial cells; amino acid metabolism; energy metabolism; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; metabolic reprogramming; pathogenesis; pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright © 2025 Dai, Liang, Li, Zhao, Li, Li, Xu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ferroptosis in pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and traditional Chinese medicine-driven therapeutic approaches.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 18;13:1598924. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1598924. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40756260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uridine alleviates the aging of alveolar epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22952. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04053-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594193 Free PMC article.
-
p38 MAPK signaling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis and inhibitor therapeutics.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 2;21(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01337-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37919729 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR signaling regulates multiple metabolic pathways in human lung fibroblasts after TGF-β and in pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025 Feb 1;328(2):L215-L228. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00189.2024. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39745695 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abedini F., Ismail M., Hosseinkhani H., Ibrahim T. A., Omar A. R., Chong P. P., et al. (2011). Effects of CXCR4 siRNA/dextran-spermine nanoparticles on CXCR4 expression and serum LDH levels in a mouse model of colorectal cancer metastasis to the liver. Cancer Manag. Res. 3, 301–309. 10.2147/CMR.S11678 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

