Long-term tuina can inhibit the occurrence of gastroparesis by protecting gastrointestinal function in diabetic rats
- PMID: 40636716
- PMCID: PMC12238824
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1536567
Long-term tuina can inhibit the occurrence of gastroparesis by protecting gastrointestinal function in diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: Diabetic gastroparesis (DGP) is a common complication in the later stage of diabetes mellitus (DM). The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect of long-term tuina on gastrointestinal (GI) function and the occurrence of DGP in diabetic rats.
Methods: Twenty healthy male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: NC, DM, DM + GT, and DM + TT. DM was induced with streptozotocin and a high-fat, high-sugar diet for 6 weeks. The DM + TT group received tuina therapy (20 min/session, 5 times/week) for 6 weeks. Weekly random blood glucose, gastric emptying rate, and small intestinal propulsion rate were measured. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining assessed gastric antrum and ileum pathology. Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS activities, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), calmodulin (CaM), and myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) mRNA and protein expressions were evaluated by PCR and Western blot. 5-HT content was measured by ELISA. Piezo2 and 5-HT4R expressions were analyzed by immunofluorescence staining to observe tuina's protective effect on GI function in DM rats.
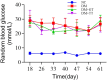
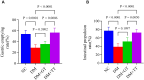
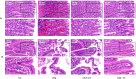
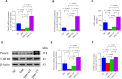
Results: Random blood glucose measurements showed normal levels in the NC group, while other groups remained above 16.7 mmol/L. The DM group exhibited reduced gastric emptying and small intestinal propulsion rates, along with gastric antrum and ileum damage. The DM + TT group showed significant improvements in gastric emptying and intestinal propulsion rates, and reduced tissue damage compared to the DM group. In the DM + TT group, mRNA and protein expressions of CaM and MLCK in antrum tissue, and nNOS, CaM, and MLCK in ileum tissue, were significantly increased. Activities of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase and CS enzymes in ileum tissue were also elevated, indicating enhanced GI function. Further analysis showed increased mRNA expressions of Piezo2 and 5-HT4R, and protein expressions of Piezo2, 5-HT, and 5-HT4R in the ileum tissues of the DM + TT group. Immunofluorescence intensity of Piezo2 and 5-HT in the ileum was also heightened. These results suggest that tuina's protective effect on GI function is related to the expression of Piezo2 ion channels.
Conclusions: Long-term tuina protects the GI function of DM rats and inhibits the occurrence of DGP, which might be related to the Piezo2/5-HT pathway.
Keywords: Piezo2/5-HT pathway; diabetes mellitus; diabetic gastroparesis; gastrointestinal function; long-term tuina.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Li, Kuang, Jiang, He, Zhang, Cao, Wang, Zhang, Tian, Zhu and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture at ST36 ameliorates gastric dysmotility in rats with diabetic gastroparesis via the nucleus tractus solitarius-vagal axis.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 7;31(21):107395. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40538511 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Data mining-based analysis to explore the application of an animal model of diabetic gastroparesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;16:1612473. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1612473. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40704142 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of Qingrun Decoction in alleviating hepatic insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic rats based on amino acid metabolism reprogramming pathways].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jun;50(12):3377-3388. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250120.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686115 Chinese.
-
Conflicting reports on the role of the glycemic effect of Catha edulis (Khat): A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:30-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.045. Epub 2016 Mar 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27025406
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

