Mind your nose: A randomized controlled trial of olfactory-based memory training for older people with subjective cognitive decline
- PMID: 40636802
- PMCID: PMC12238897
- DOI: 10.1002/trc2.70120
Mind your nose: A randomized controlled trial of olfactory-based memory training for older people with subjective cognitive decline
Abstract
Introduction: Olfactory-based cognitive training may be of benefit to individuals at risk of dementia given the strong association between olfactory impairment and cognitive decline. The Mind Your Nose (MYN) trial compared an olfactory-based memory training protocol (OMT) to a visually-based memory training protocol (VMT) among older adults with subjective cognitive decline.
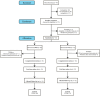
Methods: Participants (N = 53; 17 males; Mage = 72.77, standard deviation [SD] = 6.12) were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to daily OMT (n = 36) or VMT (n = 17) intervention for 20 days. Outcomes were evaluated at baseline (T0), post-intervention (T1), and 1-month follow-up (T2) and included standardized measures of global olfaction (Sniffin' Sticks) and cognition (National Institutes of Health Toolbox), as well as performance on the olfactory memory (OM) and the visual memory (VM) tasks, and measures of mood and meta-cognition.
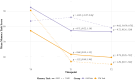
Results: A significant interaction was found between treatment allocation, time, and modality of memory task at T1(β = -37.50, p = 0.008) and T2(β = -28.75, p = 0.041). Post-hoc comparisons revealed improvement in trained tasks; OMT led to improvement on the OM task (T1; g = 0.71, p = 0.036; T2; g = 0.72, p = 0.035), and VMT led to improvement on the VM task (T1; g = 1.22, p = 0.011; T2; g = 1.29, p = 0.006). Improvement on the untrained memory task only occurred in OMT (VM task, T1; g = 0.63, p = 0.071; T2; g = 0.74, p = 0.033). No interaction between treatment allocation and time was observed post intervention or at follow-up for global olfactory ability (T1; β = 0.27, p = 0.871; T2; β = -1.27, p = 0.296).
Discussion: Consistent with previous research, transfer gains from the OMT condition to an untrained VM task suggest that olfaction may contribute to a-modal representations of memory. We argue that memory-based olfactory training offers a new frontier for cognitive interventions among those at risk of dementia.
Highlights: Relatively few cognitive training programs engage the olfactory sense.Olfactory memory training offers a new frontier of cognitive training for older adults.Olfaction may contribute to improved performance on trained and untrained tasks.The functional impact of olfactory training should be further explored.
Keywords: cognitive training, memory training, non‐pharmacological interventions; older adults, olfaction, olfactory disorders, olfactory training, smell, spatial learning, subjective cognitive decline.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-domain interventions for the prevention of dementia and cognitive decline.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 8;11(11):CD013572. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013572.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34748207 Free PMC article.
-
Reminiscence therapy for dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):CD001120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001120.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29493789 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for cognition and dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD004514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004514. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 08;(4):CD004514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004514.pub2. PMID: 14584018 Updated.
-
Algorithm-based pain management for people with dementia in nursing homes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4(4):CD013339. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013339.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35363380 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of vitamin B6 on cognition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD004393. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004393. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 14584010
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
