Social support as coping mechanism mediates the relationship between eco-anxiety and pro-environmental behavior
- PMID: 40638586
- PMCID: PMC12244539
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326931
Social support as coping mechanism mediates the relationship between eco-anxiety and pro-environmental behavior
Abstract
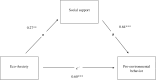
We studied social support as a coping strategy for eco-anxiety. Furthermore, we investigated the moderating or mediating role of social support in the relationship between eco-anxiety and pro-environmental behavior (PEB). The participants were Finnish adults aged 19-42. Most of the participants were women (76.2%), lived in an urban environment (82.7%), and were students (47.4%) or employees (42.8%). Data collected with an online survey was analyzed using correlation analysis, hierarchical regression analysis, and a simple mediation model. We found that experiencing eco-anxiety was positively related to PEB, and that the participants with higher social support had higher levels of eco-anxiety. In addition, using social support as a coping strategy was connected to a higher level of PEB. We found that social support mediates the positive connection between eco-anxiety and PEB, but no moderating effect was found. Our results imply that social support can be an important coping strategy for adults coping with eco-anxiety, as well as promoting PEB, offering an interesting insight for future interventions.
Copyright: © 2025 Nieminen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding Camouflaging, Stigma, and Mental Health for Autistic People in Japan.Autism Adulthood. 2025 Feb 5;7(1):52-65. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0035. eCollection 2025 Feb. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40151661
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in cancer patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 15;(8):CD006911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006911.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 12;10:CD006911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006911.pub4. PMID: 27524661 Updated.
-
Psychological interventions for asthma in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 11;1(1):CD013420. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013420.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38205864 Free PMC article.
-
An Examination of Perceived Stress and Emotion Regulation Challenges as Mediators of Associations Between Camouflaging and Internalizing Symptomatology.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Sep 16;6(3):345-361. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0121. eCollection 2024 Sep. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 39371362
References
-
- Ogunbode CA, Doran R, Hanss D, Ojala M, Salmela-Aro K, van den Broek KL. Climate anxiety, wellbeing and pro-environmental action: correlates of negative emotional responses to climate change in 32 countries. J Environ Psychol. 2022;84:101887.
-
- Hogg TL, Stanley SK, O’Brien LV, Wilson MS, Watsford CR. The hogg eco-anxiety scale: development and validation of a multidimensional scale. Global Environ Change. 2021;71:102391.
-
- Martin G, Reilly K, Everitt H, Gilliland JA. Review: the impact of climate change awareness on children’s mental well‐being and negative emotions – a scoping review. Child and Adolescent Mental Health. 2021;27(1). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

