Macrophage-derived oncostatin M repairs the lung epithelial barrier during inflammatory damage
- PMID: 40638741
- PMCID: PMC12541708
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adi8828
Macrophage-derived oncostatin M repairs the lung epithelial barrier during inflammatory damage
Abstract
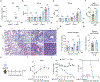
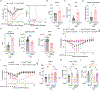
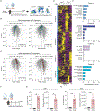
Tissue repair programs must function alongside antiviral immunity to restore the lung epithelial barrier following infection. We found that macrophage-derived oncostatin M (OSM) counteracted the pathological effects of type I interferon (IFN-I) during infection and damage in mice. At baseline, OSM-deficient mice exhibited altered alveolar type II (ATII) epithelial cell states. In response to influenza or viral mimic challenge, mice lacking OSM exhibited heightened IFN-I responses and increased mortality. OSM delivery to the lung induced ATII proliferation and was sufficient to protect deficient mice against morbidity. Furthermore, OSM promoted organoid formation despite the growth-inhibitory effects of IFN-I. These findings identify OSM as an indispensable macrophage-derived growth factor that maintains the homeostasis of lung epithelial cells and promotes their proliferation to overcome IFN-I-mediated immunopathology.
Figures

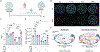
Update of
-
Macrophages control pathological interferon responses during viral respiratory infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 17:2023.12.16.572019. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.16.572019. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2025 Jul 10;389(6756):169-175. doi: 10.1126/science.adi8828. PMID: 38168230 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Högner K, Wolff T, Pleschka S, Plog S, Gruber AD, Kalinke U, Walmrath H-D, Bodner J, Gattenlöhner S, Lewe-Schlosser P, Matrosovich M, Seeger W, Lohmeyer J, Herold S, Macrophage-expressed IFN-β Contributes to Apoptotic Alveolar Epithelial Cell Injury in Severe Influenza Virus Pneumonia. Plos Pathog 9, e1003188 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

