The immunological heterogeneity of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: a systematic review
- PMID: 40639721
- PMCID: PMC12274737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tvr.2025.200323
The immunological heterogeneity of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignancy in women worldwide and generally driven by persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and adenocarcinoma (AC) are the two most common histological subtypes, with a relative increase in adenocarcinomas in the last decades. The immunological differences between cervical squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma remain largely unexplored. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing tailored therapies that can improve treatment outcomes for patients with cervical cancer. This systematic review provides an overview of the immunological features of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix.
Methods: A systematic search was performed in PubMed, Embase.com, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. All articles addressing immunological features of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix were reviewed and included based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
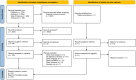
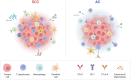
Results: In total, 3207 articles were screened, of which 43 were included. Studies show that cervical squamous cell carcinomas are characterised by a more inflamed tumour microenvironment, but also contain more regulatory T cells and immune checkpoints. In contrast, adenocarcinomas are characterised by lower immune cell infiltration, contributing to its poorer prognosis and more limited response to treatment.
Conclusion: The observed differences emphasize the need for further research into subtype-specific differences and distinct therapeutic strategies. For squamous cell carcinomas, future research should focus on combinatorial immune checkpoint blockade, including regulatory T cell-depleting strategies. For adenocarcinomas, oncolytic virotherapy, therapeutic vaccination, and oncogenic signalling interference should be explored.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Cervical cancer; Human papillomavirus; Immunotherapy; Squamous cell carcinoma; Tumour microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interventions targeted at women to encourage the uptake of cervical screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 6;9(9):CD002834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34694000 Free PMC article.
-
Primary surgery versus primary radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy for early adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;2013(1):CD006248. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006248.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23440805 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor immune composition of mismatch repair deficient and Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer: A systematic review.Cancer Treat Rev. 2024 Jun;127:102737. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102737. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024. PMID: 38669788
-
Human papillomavirus testing versus repeat cytology for triage of minor cytological cervical lesions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;2013(3):CD008054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008054.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23543559 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

