Body temperature regulates glucose metabolism and torpid behavior
- PMID: 40640117
- PMCID: PMC12246491
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61499-2
Body temperature regulates glucose metabolism and torpid behavior
Abstract
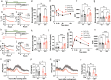
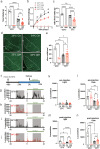
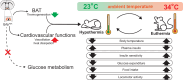
Glucose is a significant energy resource for maintaining physiological activities, including body temperature homeostasis, and glucose homeostasis is tightly regulated in mammals. Although ambient temperature tunes glucose metabolism to maintain euthermia, the significance of body temperature in metabolic regulation remains unclear owing to strict thermoregulation. Activation of Qrfp neurons in the preoptic area induced a harmless hypothermic state known as Q-neuron-induced hypothermia and hypometabolism (QIH), which is suitable for studying glucose metabolism under hypothermia. In this study, we observed that QIH mice had hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance. This glucose hypometabolic state was abolished by increasing the body temperature to euthermia. Moreover, QIH-mediated inappetence and locomotor inactivity were recovered in euthermia QIH mice. These results indicate that body temperature is considerably more powerful than ambient temperature in regulating glucose metabolism and behavior, and the glucose hypometabolism in QIH is secondary to hypothermia rather than modulated by Qrfp neurons.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
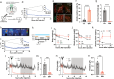
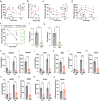
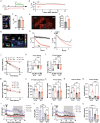
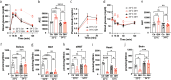
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 22KF0422/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23KF0096/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 21H02352/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H05669/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22KF0422/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 25H01025/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22K21353/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23KF0096/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H00523/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H05669/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H05769/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23H04943/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 24K23255/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H03425/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H00523/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP22K19319/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H05669/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP19dm0207078/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP24wm0625105/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP24wm0625211/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

