Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characterization of remimazolam in older Japanese adults who underwent general anesthesia at early stage of infusion
- PMID: 40640376
- PMCID: PMC12246403
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10015-z
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characterization of remimazolam in older Japanese adults who underwent general anesthesia at early stage of infusion
Abstract
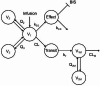
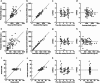
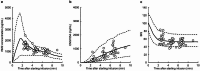
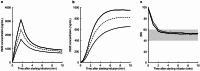
The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics of remimazolam (RMZ), a novel ultrashort-acting anesthetic, administration alone in clinical practice remain poorly understood. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between patient characteristics and the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of RMZ in older Japanese adults who underwent general anesthesia at the early stage of infusion. Plasma samples were collected from 20 patients (median age: 71.7 years; range: 42.2-88.6 years) who were intravenously administered RMZ without other anesthetics such as remifentanil or fentanyl. The pharmacokinetic profiles of RMZ and its metabolite (CNS7054) were described using three- and two-compartment models with a transit compartment, respectively. The bispectral index was selected as a clinical measure of sedation. The pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic profile of RMZ was described using a maximum inhibitory model with an effect compartment. The population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of RMZ were obtained using the nonlinear mixed-effects modeling program. RMZ clearance (CL) was increased nonlinearly with increasing body weight (BW), and the population mean CL for a typical patient (BW, 60.4 kg) was 1.38 L/min. No patient characteristics affected CNS7054 pharmacokinetics. The population mean of the half-maximal inhibitory RMZ concentration decreased nonlinearly with increasing age or BW. However, these characteristics did not meet the criteria for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic covariates. Our results suggest that BW is an intrinsic factor affecting RMZ pharmacokinetics in Japanese patients under general anesthesia in the early stages of infusion; however, no patient characteristics affected RMZ pharmacodynamics.
Keywords: Body weight; General anesthesia; Nonlinear mixed-effects modeling; Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics; Remimazolam.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The Authors K. K. and M. K. were kindly gifted remimazolam, CNS-7054, and their internal standards from Paion UK Ltd. (Richmond, United Kingdom). Other authors have no competing interest. Ethics approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Review Board of Ritsumeikan University Biwako-Kusatsu Campus (approval number BKC-IRB-2020-084) and the Ethical Review Committee of Yamagata University Faculty of Medicine (Approval number 2020–284). Consent to participate: All participants provided written informed consent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Remimazolam for Procedural Sedation in Children and Adolescents.Anesthesiology. 2025 Aug 1;143(2):368-382. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000005560. Epub 2025 May 12. Anesthesiology. 2025. PMID: 40355106 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alfentanil Enhanced the Sedation of Remimazolam During Anaesthesia Induction in Patients Undergoing Urological Day Surgery: A Randomised Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 3;19:5653-5662. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S508941. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40626102 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Effectiveness of Remimazolam in ICU Patients With Mechanical Ventilation: A Preliminary Study.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025 Jun;13(3):e70130. doi: 10.1002/prp2.70130. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40517312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of opioid, hypnotic and sedating medications on sleep-disordered breathing in adults with obstructive sleep apnoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 14;(7):CD011090. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011090.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26171909
References
-
- Leslie, K., Myles, P. S., Forbes, A. & Chan, M. T. The effect of bispectral index monitoring on long-term survival in the B-aware trial. Anesth. Analg. 110, 816–822. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181c3bfb2 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kertai, M. D. et al. Association of perioperative risk factors and cumulative duration of low bispectral index with intermediate-term mortality after cardiac surgery in the B-Unaware trial. Anesthesiology112, 1116–1127. 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d5e0a3 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Basaranoglu, G., Erden, V., Delatioglu, H. & Saitoglu, L. Reduction of pain on injection of Propofol using meperidine and remifentanil. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol.22, 890–892. 10.1017/S0265021505231502 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Li, X. et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine for Attenuation of Propofol injection pain in electroconvulsive therapy: a randomized controlled study. J. Anesth.32, 70–76. 10.1007/s00540-017-2430-3 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Bauer, T. M. et al. Prolonged sedation due to accumulation of conjugated metabolites of Midazolam. Lancet346, 145–147. 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91209-6 (1995). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

