Unveiling the therapeutic potential of senescence-related IQGAP2 in pancreatic Cancer through post-GWAS genomic and scRNA-seq analyses
- PMID: 40640432
- PMCID: PMC12245744
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03078-x
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of senescence-related IQGAP2 in pancreatic Cancer through post-GWAS genomic and scRNA-seq analyses
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a highly aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis and few treatment options available. While cellular senescence has been linked to the advancement of various cancers, its specific role in PC is not well understood.
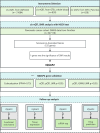
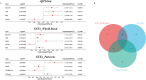
Method: We employed Mendelian randomization (MR) alongside single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to explore the involvement of senescence-associated genes (SAGs) in PC. A summary-data-based MR (SMR) analysis was performed to evaluate the connection between SAG expression and the risk of developing PC, using HEIDI test and colocalization analysis to reduce confounding variables. Additionally, scRNA-seq data were used to further examine SAG expression within pancreatic cancer cells and assess their potential as therapeutic targets.
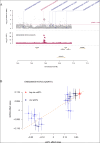
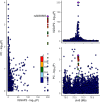
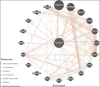
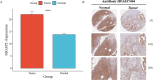
Results: The SMR analysis revealed a significant correlation between IQGAP2 expression levels and the risk of PC (P_FDR < 0.05), which was corroborated by HEIDI test (P_HEIDI > 0.01) and colocalization analysis (PPH4 = 0.79). Further MR analyses that IQGAP2 plays a causal role in PC at both genetic and protein levels. Functional enrichment analyses indicated that IQGAP2 participates in cytoskeletal organization, cell migration, signal transduction, along with pathways pertinent to PC development. The scRNA-seq findings demonstrated heightened IQGAP2 expression specifically in epithelial cells; drug prediction analyses identified it as a promising target for therapy.
Conclusion: There is a strong association between IQGAP2 and the risk factors for the progression of PC, positioning it as an attractive candidate for targeted therapies. This investigation sheds new light on mechanisms underlying PC while paving the way for precision-targeted treatment strategies.
Keywords: Cellular senescence; Drug target; IQGAP2; Pancreatic cancer; Summary-data-based MR; scRNA-seq.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics statement: Our analysis used only summary statistics and the written informed consent and approval were obtained by the respective institutional ethical review committees. Competing interests: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures



References
Grants and funding
- NO. XJTU1AF2021CRF-009/the Clinical Research Award of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
- NO. XJTU1AF2021CRF-009/the Clinical Research Award of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
- NO. XJTU1AF2021CRF-009/the Clinical Research Award of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
