Deep learning on routine full-breast mammograms enhances lymph node metastasis prediction in early breast cancer
- PMID: 40640522
- PMCID: PMC12246406
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01831-8
Deep learning on routine full-breast mammograms enhances lymph node metastasis prediction in early breast cancer
Abstract
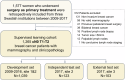
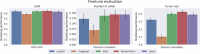
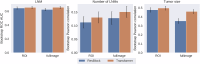
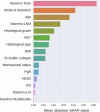
With the shift toward de-escalating surgery in breast cancer, prediction models incorporating imaging can reassess the need for surgical axillary staging. This study employed advancements in deep learning to comprehensively evaluate routine mammograms for preoperative lymph node metastasis prediction. Mammograms and clinicopathological data from 1265 cN0 T1-T2 breast cancer patients (primary surgery, no neoadjuvant therapy) were retrospectively collected from three Swedish institutions. Compared to models using only clinical variables, incorporating full-breast mammograms with preoperative clinical variables improved the ROC AUC from 0.690 to 0.774 (improvement: 0.001-0.154) in the independent test set. The combined model showed good calibration and, at sensitivity ≥90%, achieved a significantly better net benefit, and a sentinel lymph node biopsy reduction rate of 41.7% (13.0-62.6%). Our findings suggest that routine mammograms, particularly full-breast images, can enhance preoperative nodal status prediction. They may substitute key predictors such as pathological tumor size and multifocality, aiding patient stratification before surgery.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.Z. and M.D. have received speaker’s fees and travel support from Siemens Healthcare AG and are listed as patent holders for US Patent PCT/EP2014/057372. The authors otherwise declare no conflicts of interest or financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ferlay, J. et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int. J. Cancer149, 778–789 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Carter, C. L., Allen, C. & Henson, D. E. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer63, 181–187 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Caudle, A. S., Cupp, J. A. & Kuerer, H. M. Management of axillary disease. Surg. Oncol. Clin.23, 473–486 (2014). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Young researcher/The Governmental Funding of Clinical Research within the National Health Service Sweden
- 22/40304/The Governmental Funding of Clinical Research within the National Health Service Sweden
- 22/1004/The Erling Persson Foundation
- 2020-01491/The Swedish Research Council
- 2023-01-03:14/Sjöbergstiftelsen
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

