Biomarkers and therapeutic strategies targeting microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: current status and future directions
- PMID: 40640892
- PMCID: PMC12247225
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00867-4
Biomarkers and therapeutic strategies targeting microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: current status and future directions
Abstract
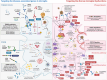
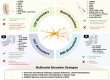
Recent advances in our understanding of non-cell-autonomous mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) have highlighted microglial dysfunction as a core driver of disease progression. Conditions such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease (PD), and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) share features of impaired microglial phagocytosis, chronic neuroinflammation, and metabolic dysregulation. These insights have prompted new therapeutic strategies targeting microglial function and emphasized the need for reliable biomarkers to monitor disease progression and treatment response. Well-established therapeutic targets, such as triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), progranulin (PGRN), and sortilin (SORT1), along with emerging candidates including LILRB4, P2Y6R, TAM receptors, and neuroinflammation-related markers, are discussed alongside novel blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and imaging biomarkers. Despite notable progress, many of these biomarkers remain restricted to preclinical studies and face translational challenges due to species-specific differences, lack of standardization, and clinical heterogeneity. Emerging technologies-including single-cell omics, spatial transcriptomics, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven integration of multimodal data-offer new opportunities to align biomarker profiles with evolving disease states and improve patient stratification. Building on the model of companion diagnostics (CDx) in oncology, integrating multimodal biomarker strategies holds promise for guiding personalized interventions, improving clinical outcomes, and deepening our mechanistic understanding of microglial contributions across the neurodegenerative spectrum.
Keywords: AD; ALS; Companion diagnostics; FTD; Microglia-targeting therapy; Microglial dysfunction; Neurodegenerative diseases; PD; Precision medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

