The cGAS-STING pathway: a dual regulator of immune response in cancer and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 40640925
- PMCID: PMC12247247
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06843-2
The cGAS-STING pathway: a dual regulator of immune response in cancer and therapeutic implications
Abstract
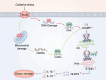
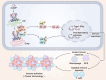
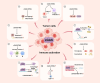
While the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway promotes anti-tumor immunity by detecting cytoplasmic DNA and inducing type I interferons, it also facilitates immune evasion through PD-L1 upregulation. Autophagy enhances cGAS signaling by delivering it to autophagosomes, boosting DNA sensing, while phase separation into liquid droplets further amplifies its activity and regulates autophagy, affecting tumor proliferation. Oxidative stress and DNA damage activate cGAS-STING, triggering pro-inflammatory cytokines that drive chronic inflammation and metabolic disorders. Interactions with immune checkpoint inhibitors augment T cell responses against tumors, yet concurrent PD-L1 induction underscores a complex balance between activation and suppression. Therapeutic strategies-combining DNA damage response inhibitors with checkpoint blockade-show promise in amplifying antitumor immunity. Moreover, post-translational modifications, including m6A methylation and acetylation, fine-tune cGAS function and downstream signaling. Together, these insights reveal the dualistic nature of cGAS-STING in cancer, offering avenues for targeted interventions that leverage its immunostimulatory potential while mitigating mechanisms of immune escape. Additionally, cGAS-driven inflammation links to metabolic dysfunction and chronic disease, underscoring its broad clinical relevance.
Keywords: Autophagy; Immune response; Therapeutic strategies; Tumor evasion; cGAS-STING pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cGAS-STING pathway in cancer immunity: dual roles, therapeutic strategies, and clinical challenges.Essays Biochem. 2025 Mar 7;69(2):EBC20253006. doi: 10.1042/EBC20253006. Essays Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40052963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, chromosome instability, and the activation of the cGAS-STING/IFN pathway in systemic sclerosis.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Aug;110:102812. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102812. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40562314 Review.
-
STING-ΔN, a novel splice isoform of STING, modulates innate immunity and autophagy in response to DNA virus infection.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 21;23(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02305-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40544261 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-modality immune nano-activator harnessing Mn2⁺ and quercetin to potentiate the cGAS-STING pathway for advanced cancer metalloimmunotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 25;23(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03336-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40128784 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS-mediated autophagy protects the liver from ischemia-reperfusion injury independently of STING.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):G655-G667. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00326.2017. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29446653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren C, Jin J, Li C, Xiang J, Wu Y, Zhou Y, et al. Metformin inactivates the cGAS-STING pathway through autophagy and suppresses senescence in nucleus pulposus cells. J Cell Sci. 2022;135(15): jcs259738. - PubMed
-
- Zhu S, Chen Q, Sun J, Du W, Chen Z, Yu M, et al. The cGAS-STING pathway promotes endometriosis by up-regulating autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;117: 109644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

