The impact of maternal health and lifestyle on low birth weight: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 40640972
- PMCID: PMC12247386
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-025-02080-x
The impact of maternal health and lifestyle on low birth weight: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: To explore maternal pregestational and periconceptional factors associated with low birth weight in offspring and inform the development of targeted interventions.
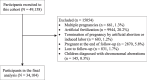
Methods: A prospective birth cohort involving 34,104 pregnant women and their offspring was constructed. The participants were enrolled during 8-14 gestational weeks and followed up at 3 months postpartum. Modified Poisson regression with robust error variances was employed to examine the associations between low birth weight and various maternal factors, including demographics, medical history, obstetric factors, lifestyle behaviors, nutrition, and environmental exposures.
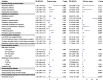
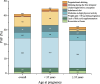
Results: The incidence of low birth weight was 8.9% (95%CI: 8.6-9.2). Maternal demographic factors, including advanced gestational age (≥ 35 years, RR = 1.14), urban residence (RR = 1.74) and a lower education level, were found to be associated with low birth weight. Pregestational medical and behavioral factors significantly increased the risk of low birth weight, including multiparity, a history of preterm birth, diseases such as tuberculosis and syphilis, and alcohol consumption (RRs: 1.71, 1.56, 2.27, 2.25, and 1.54, respectively). Additionally, periconceptional factors also significantly contributed to low birth weight, including medical factors (infections, gestational complications such as preeclampsia, a lack of folic acid supplementation; RRs: 2.36, 5.97, 1.48), nutritional factors (being underweight before conception, weight gain < 10 kg during pregnancy, imbalanced diet; RRs: 1.59, 2.42, 1.34), behavioral factors (alcohol consumption and moderate-to-high physical activity; RRs: 1.23 and 1.22), and exposure to renovation pollutants (RR = 1.21). Overall, observed modifiable risk factors accounted for 40.92% of low birth weight cases, with a greater proportion found in mothers with advanced gestational age than in those under 35 years (44.61% vs. 31.91%). Among these factors, achieving adequate weight gain during pregnancy (≥ 10 kg) could prevent 20.59% (18.68-22.45) of cases. Furthermore, the incidence of low birth weight may be effectively reduced through maintaining a balanced diet, supplementing folic acid, and avoiding excessive physical activity during pregnancy.
Conclusions: Mothers at risk for delivering low-birth-weight infants can be identified based on pregestational and periconceptional factors. This could be prevented through targeted interventions, including nutritional and behavioral measures. Tailored interventions should be prioritized by antenatal care providers.
Trial registration: The study was retrospectively registered in Chinese Clinical Trial Registry Center on 06/14/2018, registration number: ChiCTR1800016635, available at: https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.html?proj=28300 .
Keywords: Associated factor; Gestational complication; Gestational nutrition; Lifestyle behavior; Low birth weight; Population attributable fraction; Preterm birth.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Xiangya School of Public Health, Central South University (grant number: XYGW-2018–36). Written informed consent from each participant was obtained. Furthermore, it has been registered in Chinese Clinical Trial Registry Center (registration number: ChiCTR1800016635; date: 06/14/2018). Written informed consent was obtained from each participant (or legal guardian) to publish this paper. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antenatal dietary education and supplementation to increase energy and protein intake.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 2;(6):CD000032. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000032.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26031211
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-micronutrient supplementation for women during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 13;4(4):CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 14;3:CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub6. PMID: 28407219 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Multiple-micronutrient supplementation for women during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 1;2015(11):CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 13;4:CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub5. PMID: 26522344 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Incentives for increasing prenatal care use by women in order to improve maternal and neonatal outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 15;2015(12):CD009916. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009916.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26671418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wondie WT, Zeleke KA, Wubneh CA. Incidence and predictors of mortality among low birth weight neonates in the first week of life admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit in Northwestern Ethiopia comprehensive specialized hospitals, 2022. Multi-center institution-based retrospective follow-up study. BMC Pediatr. 2023;23:489. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82473644/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073653/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022JJ40207/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2022JJ10087/Outstanding Youth Scientist Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2020TJ-N07/Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Talent Support Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

