Critical emergency medicine unit: a new model to mitigate critically ill patient boarding in emergency department
- PMID: 40640984
- PMCID: PMC12247336
- DOI: 10.1186/s44158-025-00262-x
Critical emergency medicine unit: a new model to mitigate critically ill patient boarding in emergency department
Abstract
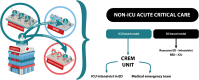
Background: Boarding of critically ill patients in the emergency department (ED) is an emerging problem that increases mortality. We have developed a "CREM Unit (critical emergency medicine unit)" led by an anesthetist-intensivist who manages critical patients directly in the ED. This study aims to assess whether the CREM Unit is an effective model for mitigating the boarding of critical patients in the ED and the impact of this on mortality.
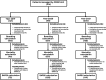
Method: This is a retrospective observational study. We collected all patients assigned to the CREM Unit from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2021. As our primary endpoints, we calculated ED boarding rate and the impact of boarding time on mortality. As a secondary endpoint, we compared observed 28-day mortality to Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) predicted mortality.
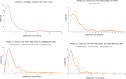
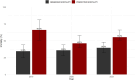
Results: Patients managed by the CREM unit were 127 in 2019, 181 in 2020, and 206 in 2021, with a clear upward trend, for a total of 514 patients (p < 0.001). Overall boarding rate was 13.9%, and length of stay in ED was not associated with an increased mortality (p = 0.399). Observed mortality was compared with expected mortality, estimated from the SAPS II score for a group of inpatients (n = 295). Moreover, the median value of SAPS II for inpatients was 54 (40.5-69.0), with an expected mortality of 55.3%, while the observed mortality was 36.8% (95% CI 31.9% to 42.1%, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Over the years, the number of patients assigned to the CREM Unit has grown steadily. These data suggest that the CREM Unit cares for a significant number of critically ill patients and could have a well-defined role both in keeping their boarding low and may contribute to reducing its impact on mortality.
Keywords: Anesthesiology; Critical care; Emergency medicine; Emergency service; Hospital mortality; Hospital/organization and administration; ICU; Lengths of stay.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: All authors have approved the manuscript for submission. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
