Late-Stage Skeletal Muscle Transcriptome in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Shows a BMP4-Induced Molecular Signature
- PMID: 40641092
- PMCID: PMC12245985
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.70005
Late-Stage Skeletal Muscle Transcriptome in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Shows a BMP4-Induced Molecular Signature
Abstract
Background: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a fatal X-linked recessive disease due to loss-of-function variants in the DYSTROPHIN gene. DMD-related skeletal muscle wasting is typified by an aberrant immune response involving upregulation of the TGFβ family of cytokines, like TGFβ1 and BMP4. We previously demonstrated that bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) is increased in DMD and BMP4 stimulation induces a 20-fold upregulation of Smad8 transcription in muscle cells. However, the role of BMP4 in late-stage DMD skeletal muscle is unknown. We hypothesized that BMP4 signalling is a driver of aberrant gene expression in late-stage human DMD skeletal muscle detectable by a transcriptomic signature.
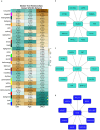
Methods: Transcriptomes from skeletal muscle biopsies of late-stage DMD versus non-DMD controls and C2C12 muscle cells with or without BMP4 stimulation were generated using RNA-Seq. We tested transcriptional differences at the single transcript level in skeletal muscle biopsy samples from three patients with DMD and compared them to three non-DMD. They were then analyzed by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, weighted gene coexpression network analyses (WGCNA) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). Key hub and high-fold change genes overlapping in the DMD and BMP4 muscle transcriptomes were validated in additional primary and bulk skeletal muscle samples.
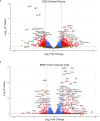
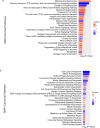
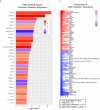
Results: A total of 3048 transcripts in the human muscle and 5291 transcripts in C2C12 muscle cells were differentially expressed. WGCNA identified an overlapping molecular signature of 1027 genes dysregulated in DMD muscle that were induced in BMP4-stimulated C2C12 muscle cells. SERPING1 and Aff3 were identified as the top hub genes. Highly upregulated DMD muscle transcripts that overlapped with BMP4-stimulated C2C12 muscle cells included ADAM12, SERPING1, SMAD8 and SFRP4. DMD skeletal muscle analysis showed aberrant upregulation of TGFβ signalling, extracellular matrix remodelling and collagen biosynthesis pathways, in contrast to inhibited mitochondrial and metabolic pathways.
Conclusions: In summary, the DMD transcriptome was characterized by dysregulation of immune function, ECM remodelling and muscle bioenergetic metabolism. We additionally define a late-stage DMD skeletal muscle transcriptome that overlaps with a BMP4-induced molecular signature in C2C12 muscle cells. This supports BMP4/Smad8 pathway as a disease-driving regulator of transcriptomic changes in late-stage DMD skeletal muscle. Further exploration of this cross-species transcriptomic signature may expand our understanding of the evolution of dystrophic signalling pathways and the associated gene networks, which could be evaluated for therapeutic development.
Keywords: BMP4; SMAD8; TGFβ1; Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
M.A.L. served as Principal Investigator on a clinical trial and participated in scientific advisory boards for Sarepta Therapeutics Inc. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Late-Stage Skeletal Muscle Transcriptome in Duchenne muscular dystrophy shows a BMP4-Induced Molecular Signature.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 25:2024.04.19.590266. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.19.590266. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Aug;16(4):e70005. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.70005. PMID: 38712206 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hoffman E. P., R. H. Brown, Jr. , and Kunkel L. M., “Dystrophin: The Protein Product of the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Locus,” Cell 51, no. 6 (1987): 919–928. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. W., Nagaraju K., Bakay M., et al., “Early Onset of Inflammation and Later Involvement of TGFbeta in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy,” Neurology 65, no. 6 (2005): 826–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL153460/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS092651/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS111275-01/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX006231/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- BX006231/VA/VA/United States
- K08-NS120812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD095897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- BX004419/VA/VA/United States
- T32 UAB Center for Exercise Medicine
- R01HD095897/National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- R21 NS111275/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS140497/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UAB Center for Exercise Medicine
- R01 NS092651/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS140497/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS120812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004419/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

