Potential Antifungal Effects of Calcium Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanosuspension on Mycelial Growth of Neoscytalidium dimidiatum (Ascomycota, Botryosphaeriaceae) Associated With Pistachio Dieback
- PMID: 40641104
- PMCID: PMC12245995
- DOI: 10.1111/1758-2229.70144
Potential Antifungal Effects of Calcium Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanosuspension on Mycelial Growth of Neoscytalidium dimidiatum (Ascomycota, Botryosphaeriaceae) Associated With Pistachio Dieback
Abstract
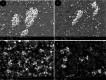
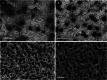
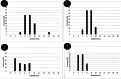
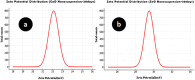
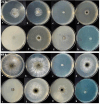
The study aimed to synthesise and evaluate the efficacy of calcium oxide (CaO) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nano-suspensions, in conjunction with adjuvants, on the mycelial growth of Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, a notable fungal pathogen impacting pistachio trees in Iran. The study tackles a significant agricultural challenge by exploring eight different treatments, including both nano and pure forms of calcium oxide (CaO) and zinc oxide (ZnO), as well as polyethylene glycol, peracetic acid, and copper oxychloride. The results indicated a notable reduction in mycelial growth, particularly with the zinc oxide nanosuspension, especially when used in combination with peracetic acid, which revealed a synergistic antifungal effect. Further research is necessary to assess the field applications of these treatments for sustainable plant disease management.
Keywords: Neoscytalidium; foliar fertiliser; fungicide; mycelial growth; nanosuspension; synergistic effects.
© 2025 The Author(s). Environmental Microbiology Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwal, H. , Kumar S. V., and Rajeshkumar S.. 2017. “A Review on Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles‐An Eco‐Friendly Approach.” Resource‐Efficient Technologies 3, no. 4: 406–413.
-
- Akhtari, A. , Davari M., Habibi Yangjeh A., Ebadollahi A., and Feizpur S.. 2022. “Antifungal Activities of Pure and ZnO‐Encapsulated Essential Oil of Zataria Multiflora on Alternaria Solani as the Pathogenic Agent of Tomato Early Blight Disease.” Frontiers in Plant Science 13: 932475. 10.3389/fpls.2022.932475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Raish, S. M. , Saeed E. E., Sham A., Alblooshi K., El‐Tarabily K. A., and AbuQamar S. F.. 2020. “Molecular Characterization and Disease Control of Stem Canker on Royal Poinciana (Delonix Regia) Caused by Neoscytalidium Dimidiatum in The United Arab Emirates.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21: 1033. 10.3390/ijms21031033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

