Synthesis and Characterization of Gum Kondagogu Stabilized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Application as an Antibacterial Agent Against Wastewaterborne Bacteria
- PMID: 40641154
- PMCID: PMC12246657
- DOI: 10.1111/apm.70046
Synthesis and Characterization of Gum Kondagogu Stabilized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Application as an Antibacterial Agent Against Wastewaterborne Bacteria
Abstract
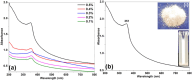
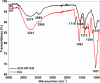
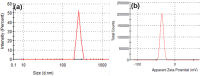
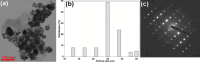
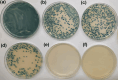
Wastewater recycling is one of the viable options for attaining sustainable water management. In this scenario, gum stabilized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NP) were synthesized employing the alkaline precipitation method with gum kondagogu stabilizer. Synthesized NP were characterized using UV-vis, DLS, zeta potential, XRD, FTIR, and TEM. ZnO NP exhibited an absorption peak at 351 nm in UV-vis, a zeta potential value of-35 mV, and a z-average value of 254 nm in DLS. XRD pattern showed a characteristic hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure and FTIR data indicated the capping of NP by various gum functional groups. The size of spherical NP varied from 12.4 to 35.7 nm, and the mean particle size was 24.8 ± 5.1 nm. The in vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO NP against wastewaterborne bacteria, Escherichia coli (Gram- negative) and Bacillus subtilis (Gram-positive) was studied with the resazurin broth assay. MIC values of 900 μg/mL and 900 μg/mL and MBC values of 1800 μg/mL and 900 μg/mL of ZnO NP were recorded towards E. coli and B. subtilis. Notably, ZnO NP exhibited superior bactericidal activity against B. subtilis compared to previous studies. Thus, the current study on ZnO NP mediated bacterial disinfection has wide applications in wastewater treatment and remediation of microbially contaminated effluents.
Keywords: antibacterial; tree gum; water disinfection; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
© 2025 The Author(s). APMIS published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of APMIS ‐ Journal of Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Microwave assisted starch stabilized green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 2;15(1):28288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14193-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40753352 Free PMC article.
-
Biological activities of optimized biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Proteus mirabilis PQ350419 alone or combined with chitosan and ampicillin against common multidrug-resistant bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jul 5;24(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02783-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40618114 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Asplenium dalhousiae and their potential biological properties.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 30;20(6):e0325533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325533. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40587502 Free PMC article.
-
Application of nano-ZnO in the food preservation industry: antibacterial mechanisms, influencing factors, intelligent packaging, preservation film and safety.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(22):4327-4353. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2387327. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39097753 Review.
-
Nano-pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of green-synthesized ZnO nanoparticles: a pathway to safer therapeutic applications.Xenobiotica. 2025 Apr;55(4):265-276. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2025.2505062. Epub 2025 May 21. Xenobiotica. 2025. PMID: 40380770 Review.
References
-
- Chopra M., Bernela M., Kaur P., Manuja A., Kumar B., and Thakur R., “Alginate/Gum Acacia Bipolymeric Nanohydrogels–Promising Carrier for Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 72 (2015): 827–833. - PubMed
-
- Kora A. J., “Applications of Inorganic Metal Oxide and Metal Phosphate‐Based Nanoceramics in Dentistry,” in Industrial Applications of Nanoceramics: A Volume in Micro and Nano Technologies, ed. Mallakpour S. and Hussain C. M. (Elsevier Publishing, 2024).
-
- Mohamed A. A., Abu‐Elghait M., Ahmed N. E., and Salem S. S., “Eco‐Friendly Mycogenic Synthesis of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles for In Vitro Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antifungal Applications,” Biological Trace Element Research 199 (2021): 2788–2799. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

