ATF3 Deficiency Exacerbates Ageing-Induced Atherosclerosis and Clinical Intervention Strategy
- PMID: 40641410
- PMCID: PMC12499416
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502249
ATF3 Deficiency Exacerbates Ageing-Induced Atherosclerosis and Clinical Intervention Strategy
Abstract
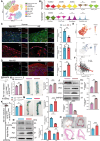
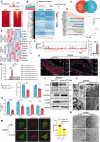
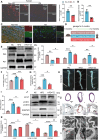
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) senescence is a pivotal driver of atherosclerosis (AS), but molecular links to ageing-related dysfunction are unclear. It is aimed to identify regulators of VSMC senescence and develop clinical interventions for ageing-related AS. Using single-cell RNA sequencing of human atherosclerotic carotid arteries and immunofluorescence validation, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) is identified as central to VSMC senescence. Mechanistic studies employ SMC-specific ATF3 knockout mice, CUT&Tag-seq, RNA/protein interaction assays, and m6A epitranscriptomic analyses. To bridge discovery to therapy, high-throughput virtual screening is performed for ATF3-targeting compounds and functionally validated hits. ATF3 deficiency in VSMCs accelerates ageing-induced AS by promoting senescence. Multi-omics showed ATF3 activates ATG7, triggering autophagy, while cytoplasmic ATG7 enhances ATF3 nuclear translocation, establishing a positive feedback loop. Ageing increases m6A methylation and decreases the stability of Atf3 mRNA. Terazosin (TZ) diminishes the interaction between YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein F2 (YTHDF2) and Atf3 mRNA, helping to preserve Atf3 mRNA stability. TZ is a promising therapeutic strategy for delaying VSMC senescence and preventing AS. ATF3 protects against VSMC senescence and AS by orchestrating autophagy via a novel ATF3-ATG7 amplification loop. Repurposing TZ to stabilize ATF3 offers a translatable approach to combat ageing-driven cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: activated transcription factor 3; atherosclerosis; autophagy; terazosin; vascular smooth muscle cells senescence.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
