Humanized mouse model reveals T cell ANXA2 as a potential therapeutic target in ischemic stroke
- PMID: 40641552
- PMCID: PMC12245446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112302
Humanized mouse model reveals T cell ANXA2 as a potential therapeutic target in ischemic stroke
Abstract
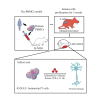
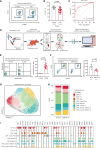
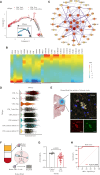
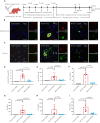
Stroke T cell studies in rodents have not been translated to human studies. The mechanism of cellular and molecular T cells changes after stroke remains incompletely understood. Thus, this study established a humanized mouse model after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and identifies potential therapeutic targets of humanized T cell populations. Similar to patients with stroke, a proportion of T cells was decreased in peripheral blood of humanized T cell stroke mice. Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), we identified Annexin A2 (ANXA2) as biomarker of humanized T cell subsets in MCAO, which was validated using human ischemic brain and peripheral blood. With small-molecule inhibitors Leu-Cys-Lys-Leu-Ser-Leu (LCKLSL), ANXA2 inhibition altered TCM and TEM subset in humanized mice. Furthermore, LCKLSL exhibited a neuroprotective role against ischemic damage, mitigating neuroinflammation, inhibiting T cell infiltration, and decreasing pro-inflammatory factors. Hence, this humanized T cell ischemic stroke model is more representative of the human disease than previous models; furthermore, ANXA2 is a meaningful therapeutic target.
Keywords: Model organism; Molecular neuroscience.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Owolabi M.O., Thrift A.G., Martins S., Johnson W., Pandian J., Abd-Allah F., Varghese C., Mahal A., Yaria J., Phan H.T., et al. The state of stroke services across the globe: Report of World Stroke Organization-World Health Organization surveys. Int. J. Stroke. 2021;16:889–901. doi: 10.1177/17474930211019568. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

