A Multi-Analytical Exploration of Flavored Black Teas: Profiling Volatile Compounds, Caffeine Content, and Biological Effects
- PMID: 40641566
- PMCID: PMC12241430
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70585
A Multi-Analytical Exploration of Flavored Black Teas: Profiling Volatile Compounds, Caffeine Content, and Biological Effects
Abstract
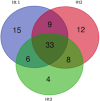
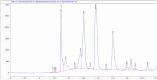
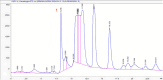
This study aims at investigating the phytochemistry and biological effects of three different flavored black teas from Sweden. Analyses were conducted using gas and liquid chromatography. The major volatile compounds of all the tea samples were found to be linalyl acetate and α-terpineol. HPLC results indicated caffeine levels of 1.08%, 1.46%, and 1.18% in samples Ht1, Ht2, and Ht3, respectively. Ht1 exhibited the highest antioxidant activity, particularly in DPPH· and ABTS+ radical scavenging capacities (0.15 and 0.21 mgTE/g, respectively). Additionally, Ht1 also showed higher antioxidant activity than the other samples in both CUPRAC and FRAP tests. Metal chelation capacity was highest in Ht3, suggesting significant chelation potential due to nonphenolic components. Ht1 showed strong inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (1.21 mg GALAE/g), butyrylcholinesterase (3.48 mg GALAE/g), and tyrosinase (1.47 mg KAE/g) enzymes. It highlights valuable insights into how different flavor additives may influence the health benefits of tea.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; caffeine content; enzyme inhibition; flavored black tea; volatile compounds.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unveiling the ethnomedicinal potential of Alchemilla speciosa Buser: An underexplored source of bioactive compounds for skin health.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120068. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120068. Epub 2025 May 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40451493
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ibuprofen and/or paracetamol (acetaminophen) for pain relief after surgical removal of lower wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 12;2013(12):CD004624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004624.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24338830 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Ağalar, H. G. , Demirci B., Demirci F., and Kırımer N.. 2017. “The Volatile Compounds of the Elderflowers Extract and the Essential Oil.” Records of Natural Products 11, no. 5: 491–496. 10.25135/rnp.63.16.08.058. - DOI
-
- Bae, I. K. , Ham H. M., Jeong M. H., Kim D. H., and Kim H. J.. 2015. “Simultaneous Determination of 15 Phenolic Compounds and Caffeine in Teas and Mate Using RP‐HPLC/UV Detection: Method Development and Optimization of Extraction Process.” Food Chemistry 172: 469–475. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.050. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Demirci, B. , Kırcı D., Öztürk G., and Demirci F.. 2022. “Effect of Extraction Time on Origanum onites L. Infusions and Essential Oils–Biological Evaluation, Statistical Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analyses.” Chemistry & Biodiversity 19, no. 12: e202200482. 10.1002/cbdv.202200482. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

