Three new species of Neopestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis (Sporocadaceae, Amphisphaeriales) associated with shrub leaf diseases from Fujian, China
- PMID: 40641593
- PMCID: PMC12238990
- DOI: 10.3897/mycokeys.119.148647
Three new species of Neopestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis (Sporocadaceae, Amphisphaeriales) associated with shrub leaf diseases from Fujian, China
Abstract
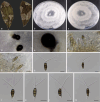
Neopestalotiopsis and Pseudopestalotiopsis are classified as pestalotioid fungi, include a diverse range of plant pathogenic, endophytic and saprobic species and are widely distributed in tropical and temperate climates. These fungi are associated with a wide variety of plants worldwide and are exemplified by multi-septate conidia with appendages at both ends. Phytopathogenic members cause various plant diseases, for example, leaf spot, fruit rot, canker, blight and various infections affecting palm, mango, blueberry, tea and other important crops. In this study, six isolates were collected from diseased leaves of Litseaverticillata, Ixorachinensis and an unidentified shrub in Fujian Province, China. Based on morphological characteristics and molecular phylogenetic analyses of combined nucleotide sequences of internal transcribed spacer regions of rDNA (ITS), the partial translation elongation factor 1-alpha gene (tef1) and partial beta-tubulin gene (tub2), three new species Neopestalotiopsislitseae sp. nov., Neo.longqishanensis sp. nov. and Pseudopestalotiopsiszhangzhouensis sp. nov. are described and illustrated herein.
Keywords: Morphology; multigene phylogeny; new taxa; pestalotioid fungi.
Zhi-Ang Heng, Tai-Chang Mu, Nemat O. Keyhani, Li-Xia Yang, Ming-Hai Zheng, Hua-Jun Lv, Zhi-Ying Zhao, Yu-Chen Mao, Jun-Ya Shang, Jiao Yang, Hui-Li Pu, Yong-Sheng Lin, Meng-Jia Zhu, Yu-Xiao Dang, Dong-Mei Wu, Zhen-Xing Qiu, Jun-Zhi Qiu, Xia-Yu Guan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel endophytic pestalotioid species associated with Itea in Thailand.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 3;15:1532712. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1532712. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40248370 Free PMC article.
-
Hidden diversity of Pestalotiopsis and Neopestalotiopsis (Amphisphaeriales, Sporocadaceae) species allied with the stromata of entomopathogenic fungi in Taiwan.MycoKeys. 2024 Jan 31;101:275-312. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.101.113090. eCollection 2024. MycoKeys. 2024. PMID: 38333551 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic and Morphological Evidence for Three New Species of Diaporthales (Ascomycota) from Fujian Province, China.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 May 27;10(6):383. doi: 10.3390/jof10060383. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921368 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of the root rot of Ardisia crenate caused by Neofusicoccum parvum in China.Plant Dis. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-03-25-0656-PDN. Online ahead of print. Plant Dis. 2025. PMID: 40587187
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmmed MS, Sikder MM, Sarker SR, Hossain MS, Shubhra RD, Alam N. (2022) First report of Pseudopestalotiopsistheae causing Aloevera leaf spot disease in Bangladesh. American Journal of Plant Sciences 13(2): 193–204. 10.4236/ajps.2022.132012 - DOI
-
- Barr ME. (1975) The genus Ostreichnion. Mycotaxon 3(1): 81–88. 10.5962/p.413961 - DOI
-
- Bezerra JDP, Machado AR, Firmino AL, Rosado AWC, Souza CAFd, Souza-Motta CMd, Freire KTLdS, Paiva LM, Magalhães OMC, Pereira OL, Crous PW, Oliveira TGLd, Abreu VPd, Fan X. (2018) Mycological Diversity Description I. Acta Botanica Brasilica 32: 656–666. 10.1590/0102-33062018abb0154 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
